Switching off key signaling survival molecules to switch on the resolution of inflammation
- PMID: 25136148
- PMCID: PMC4127222
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/829851
Switching off key signaling survival molecules to switch on the resolution of inflammation
Abstract
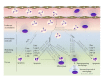
Inflammation is a physiological response of the immune system to injury or infection but may become chronic. In general, inflammation is self-limiting and resolves by activating a termination program named resolution of inflammation. It has been argued that unresolved inflammation may be the basis of a variety of chronic inflammatory diseases. Resolution of inflammation is an active process that is fine-tuned by the production of proresolving mediators and the shutdown of intracellular signaling molecules associated with cytokine production and leukocyte survival. Apoptosis of leukocytes (especially granulocytes) is a key element in the resolution of inflammation and several signaling molecules are thought to be involved in this process. Here, we explore key signaling molecules and some mediators that are crucial regulators of leukocyte survival in vivo and that may be targeted for therapeutic purposes in the context of chronic inflammatory diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Medzhitov R. Inflammation 2010: new adventures of an old flame. Cell. 2010;140(6):771–776. - PubMed
-
- Katzenstein AA, Myers JL. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Clinical relevance of pathologic classification. The American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 1998;157(4):1301–1315. - PubMed
-
- Gilroy DW, Lawrence T, Perretti M, Rossi AG. Inflammatory resolution: new opportunities for drug discovery. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2004;3(5):401–416. - PubMed
-
- Serhan CN, Savill J. Resolution of inflammation: the beginning programs the end. Nature Immunology. 2005;6(12):1191–1197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

