Early prediction of preeclampsia
- PMID: 25136369
- PMCID: PMC4127237
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/297397
Early prediction of preeclampsia
Abstract
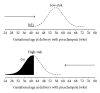
Effective screening for the development of early onset preeclampsia (PE) can be provided in the first-trimester of pregnancy. Screening by a combination of maternal risk factors, uterine artery Doppler, mean arterial pressure, maternal serum pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A, and placental growth factor can identify about 95% of cases of early onset PE for a false-positive rate of 10%.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prenatal screening for preeclampsia: the roles of placental growth factor and pregnancy-associated plasma protein A in the first trimester and placental growth factor and soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1-placental growth factor ratio in the early second trimester.AJOG Glob Rep. 2023 Mar 11;3(2):100193. doi: 10.1016/j.xagr.2023.100193. eCollection 2023 May. AJOG Glob Rep. 2023. PMID: 37168546 Free PMC article.
-
First-trimester screening for early and late preeclampsia using maternal characteristics, biomarkers, and estimated placental volume.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Jan;218(1):126.e1-126.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2017.10.024. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018. PMID: 29097177
-
First trimester preeclampsia screening and prediction.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Feb;226(2S):S1071-S1097.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.07.020. Epub 2020 Jul 16. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022. PMID: 32682859 Review.
-
Prediction of preeclampsia throughout gestation with maternal characteristics and biophysical and biochemical markers: a longitudinal study.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Jan;226(1):126.e1-126.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2021.01.020. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022. PMID: 34998477 Free PMC article.
-
First-trimester maternal factors and biomarker screening for preeclampsia.Prenat Diagn. 2014 Jul;34(7):618-27. doi: 10.1002/pd.4397. Epub 2014 May 21. Prenat Diagn. 2014. PMID: 24764257 Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of Roles of Uterine Artery Doppler in Pregnancy Complications.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 3;9:813343. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.813343. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35308523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction and function of a fusion protein consisting of a single‑chain variable fragment and RBP4.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Jul;20(1):671-677. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10270. Epub 2019 May 22. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31115584 Free PMC article.
-
Network-Based Analysis Reveals Novel Biomarkers in Peripheral Blood of Patients With Preeclampsia.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jun 16;9:757203. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.757203. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35782866 Free PMC article.
-
Pregestational maternal risk factors for preterm and term preeclampsia: A population-based cohort study.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2023 Nov;102(11):1549-1557. doi: 10.1111/aogs.14642. Epub 2023 Jul 25. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2023. PMID: 37491773 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Preterm Birth Using Proteomics.Clin Perinatol. 2024 Jun;51(2):391-409. doi: 10.1016/j.clp.2024.02.011. Epub 2024 Mar 23. Clin Perinatol. 2024. PMID: 38705648 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Make Every Mother and Child Count. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2005. (World Health Report, 2005).
-
- Confidential Enquiry into Maternal and Child Health (CEMACH) Perinatal Mortality 2006. England, Wales and Northern Ireland. London, UK: CEMACH; 2008.
-
- Duley L. The global impact of pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. Seminars in Perinatology. 2009;33(3):130–137. - PubMed
-
- Yu CKH, Khouri O, Onwudiwe N, Spiliopoulos Y, Nicolaides KH. Prediction of pre-eclampsia by uterine artery Doppler imaging: relationship to gestational age at delivery and small-for-gestational age. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology. 2008;31(3):310–313. - PubMed
-
- Witlin AG, Saade GR, Mattar F, Sibai BM. Predictors of neonatal outcome in women with severe preeclampsia or eclampsia between 24 and 33 weeks' gestation. The American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2000;182(3):607–611. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

