Does platelet-rich plasma freeze-thawing influence growth factor release and their effects on chondrocytes and synoviocytes?
- PMID: 25136613
- PMCID: PMC4124719
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/692913
Does platelet-rich plasma freeze-thawing influence growth factor release and their effects on chondrocytes and synoviocytes?
Abstract
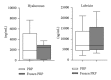
PRP cryopreservation remains a controversial point. Our purpose was to investigate the effect of freezing/thawing on PRP molecule release, and its effects on the metabolism of chondrocytes and synoviocytes. PRP was prepared from 10 volunteers, and a half volume underwent one freezing/thawing cycle. IL-1β, HGF, PDGF AB/BB, TGF-β1, and VEGF were assayed 1 hour and 7 days after activation. Culture media of chondrocytes and synoviocytes were supplemented with fresh or frozen PRP, and, at 7 days, proliferation, gene expression, and secreted proteins levels were evaluated. Results showed that in the freeze-thawed PRP the immediate and delayed molecule releases were similar or slightly lower than those in fresh PRP. TGF-β1 and PDGF AB/BB concentrations were significantly reduced after freezing both at 1 hour and at 7 days, whereas HGF concentration was significantly lower in frozen PRP at 7 days. In fresh PRP IL-1β and HGF concentrations underwent a significant further increase after 7 days. Similar gene expression was found in chondrocytes cultured with both PRPs, whereas in synoviocytes HGF gene expression was higher in frozen PRP. PRP cryopreservation is a safe procedure, which sufficiently preserves PRP quality and its ability to induce proliferation and the production of ECM components in chondrocytes and synoviocytes.
Figures


References
-
- Filardo G, Presti ML, Kon E, Marcacci M. Nonoperative biological treatment approach for partial achilles tendon lesion. Orthopedics. 2010;33(2):120–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

