Rectal sensitivity in diabetes patients with symptoms of gastroparesis
- PMID: 25136644
- PMCID: PMC4130227
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/784841
Rectal sensitivity in diabetes patients with symptoms of gastroparesis
Abstract
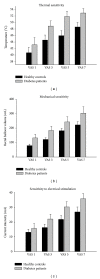
In a clinical setting, diabetic autonomic complications (cardiac, gastrointestinal, urogenital, etc.) are often handled as separate entities. We investigated rectal sensitivity to heat, mechanical distension, and electrical stimulations in 20 patients with diabetes and symptoms of gastroparesis, to evaluate the extent of visceral neuronal damage. Furthermore, to evaluate the relation between the nervous structures we examined gastric emptying and cardiac autonomic function with the hypothesis being an association between these. We found that 60% of patients had delayed gastric empting. Rectal hyposensitivity was a general finding as they tolerated 67% higher thermal, 42% more mechanical, and 33% higher electrical current intensity compared to healthy controls. In patients, most heart rate variability parameters were reduced; they reported significantly more gastrointestinal symptoms and a reduced quality of life in all SF-36 domains. Shortened RR interval correlated with reduced rectal temperature sensitivity, and gastric retention rate was negatively associated with symptoms of nausea and vomiting. To conclude, in these patients with signs and symptoms of diabetic gastroparesis, rectal sensitivity was reduced, and heart rate variability was impaired. Thus, we suggest regarding diabetic autonomic neuropathy as a diffuse disorder. Symptoms of widespread autonomic dysfunction and sensory disorders should be expected and treated in these patients.
Figures
References
-
- Bytzer P, Talley NJ, Leemon M, Young LJ, Jones MP, Horowitz M. Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms associated with diabetes mellitus: A population-based survey of 15000 adults. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2001;161(21):1989–1996. - PubMed
-
- Ko GTC, Chan W-B, Chan JCN, Tsang LWW, Cockram CS. Gastrointestinal symptoms in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetic Medicine. 1999;16(8):670–674. - PubMed
-
- Lelic D, Brock C, Søfteland E, et al. Brain networks encoding rectal sensation in type 1 diabetes. Neuroscience. 2013;237:96–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

