Circulating miR-19a and miR-205 in serum may predict the sensitivity of luminal A subtype of breast cancer patients to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with epirubicin plus paclitaxel
- PMID: 25137071
- PMCID: PMC4138038
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104870
Circulating miR-19a and miR-205 in serum may predict the sensitivity of luminal A subtype of breast cancer patients to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with epirubicin plus paclitaxel
Erratum in
-
Correction: Circulating miR-19a and miR-205 in Serum May Predict the Sensitivity of Luminal A Subtype of Breast Cancer Patients to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy with Epirubicin Plus Paclitaxel.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 25;10(8):e0136826. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136826. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26305791 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The luminal A subtype of breast cancer has a good prognosis and is sensitive to endocrine therapy but is less sensitive to chemotherapy. It is necessary to identify biomarkers to predict chemosensitivity and avoid over-treatment. We hypothesized that miRNAs in the serum might be associated with chemosensitivity.
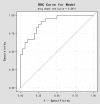
Methods: Sixty-eight breast cancer patients received neoadjuvant chemotherapy with epirubicin plus paclitaxel. The serum of the patients was collected before chemotherapy and stored at -80°C. The samples were classified into two groups in term of the chemosensitivity. We identified the differential expression patterns of miRNAs between the chemotherapy sensitive and resistant groups using microRNA profiling. Four miRNAs that were differentially expressed between the two groups were further validated in another 56 samples. We created a model fitting formula and a receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve using logistic regression analysis to evaluate the prediction potency.
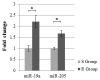
Results: We identified 8 miRNAs differentially expressed between the two groups: 6 miRNAs were up-regulated, and 2 miRNAs were down-regulated in the resistant group compared with the sensitive group. The expression of miR-19a and miR-205 were determined to have significant differences between the two groups (P<0.05). A predictive model of these two miRNAs was created by the logistic regression analysis. The probability of this model was 89.71%. Based on the ROC curve, the specificity was 75.00%, and the sensitivity was 81.25%.
Conclusions: The combination of miR-19a and miR-205 in the serum may predict the chemosensitivity of luminal A subtype of breast cancer to epirubicin plus paclitaxel neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plasma microRNAs Predict Chemoresistance in Patients With Metastatic Breast Cancer.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Jan 1;18:1533033819828709. doi: 10.1177/1533033819828709. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 30786836 Free PMC article.
-
Serum miR-21 and miR-125b as markers predicting neoadjuvant chemotherapy response and prognosis in stage II/III breast cancer.Hum Pathol. 2017 Jun;64:44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2017.03.016. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Hum Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28412211
-
Dynamics of circulating microRNAs as a novel indicator of clinical response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer.Cancer Med. 2018 Sep;7(9):4420-4433. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1723. Epub 2018 Aug 11. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 30099860 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miR-1246 and miR-155 as predictive and prognostic biomarkers for trastuzumab-based therapy resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2020 Dec;86(6):761-772. doi: 10.1007/s00280-020-04168-z. Epub 2020 Oct 17. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33068176
-
Identification of miRNA Signature in Breast Cancer to Predict Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Response.Pathol Oncol Res. 2021 Apr 30;27:1609753. doi: 10.3389/pore.2021.1609753. eCollection 2021. Pathol Oncol Res. 2021. PMID: 34257614 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Metastatic breast cancer: the potential of miRNA for diagnosis and treatment monitoring.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015 Mar;34(1):145-55. doi: 10.1007/s10555-015-9551-7. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015. PMID: 25721950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating miRNAs in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 7;14(9):2317. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092317. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma microRNAs Predict Chemoresistance in Patients With Metastatic Breast Cancer.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Jan 1;18:1533033819828709. doi: 10.1177/1533033819828709. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 30786836 Free PMC article.
-
miR-205 in Breast Cancer: State of the Art.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 22;22(1):27. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010027. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33375067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abnormal serum microRNA profiles in tuberous sclerosis are normalized during treatment with everolimus: possible clinical implications.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2016 Sep 29;11(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s13023-016-0512-1. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2016. PMID: 27680012 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coates AS, Colleoni M, Goldhirsch A (2012) Is adjuvant chemotherapy useful for women with luminal a breast cancer? J Clin Oncol 30: 1260–1263. - PubMed
-
- Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, et al. (2005) MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 65: 7065–7070. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

