Effect of different human papillomavirus serological and DNA criteria on vaccine efficacy estimates
- PMID: 25139208
- PMCID: PMC4157699
- DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwu168
Effect of different human papillomavirus serological and DNA criteria on vaccine efficacy estimates
Abstract
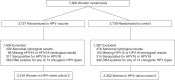
Two trials of clinically approved human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccines, Females United to Unilaterally Reduce Endo/Ectocervical Disease (FUTURE I/II) and the Papilloma Trial Against Cancer in Young Adults (PATRICIA), reported a 22% difference in vaccine efficacy (VE) against cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 or worse in HPV-naïve subcohorts; however, serological testing methods and the HPV DNA criteria used to define HPV-unexposed women differed between the studies. We applied previously described methods to simulate these HPV-naïve subcohorts within the Costa Rica HPV16/18 Vaccine Trial and assessed how these criteria affect the estimation of VE. We applied 2 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) thresholds for HPV16 and HPV18 seropositivity (8 and 7 ELISA units/mL, respectively, for PATRICIA; 54 and 65 ELISA units/mL, respectively, for FUTURE I/II (to approximate the competitive Luminex immunoassay)) and 2 criteria for HPV DNA positivity (12 oncogenic HPV types, plus HPV66 and 68/73 for PATRICIA; or plus HPV6 and 11 for FUTURE I/II). VE was computed in the 2 naïve subcohorts. Using the FUTURE I/II and PATRICIA criteria, VE estimates against cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 or worse, regardless of HPV type, were 69.0% (95% confidence interval: 40.3%, 84.9%) and 80.8% (95% confidence interval: 52.6%, 93.5%), respectively (P = 0.1). Although the application of FUTURE I/II criteria to our cohort resulted in the inclusion of more sexually experienced women, methodological differences did not fully explain the VE differences.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00128661.
Keywords: human papillomavirus; methodological differences; naïve population; vaccine efficacy.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health 2014. This work is written by (a) US Government employee(s) and is in the public domain in the US.
Figures

References
-
- Hildesheim A, Herrero R, Wacholder S, et al. Effect of human papillomavirus 16/18 L1 viruslike particle vaccine among young women with preexisting infection: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2007;298(7):743–753. - PubMed
-
- Muñoz N, Kjaer SK, Sigurdsson K, et al. Impact of human papillomavirus (HPV)-6/11/16/18 vaccine on all HPV-associated genital diseases in young women. JNatl Cancer Inst. 2010;102(5):325–339. - PubMed
-
- Lehtinen M, Paavonen J, Wheeler CM, et al. Overall efficacy of HPV-16/18 AS04-adjuvanted vaccine against grade 3 or greater cervical intraepithelial neoplasia: 4-year end-of-study analysis of the randomised, double-blind PATRICIA Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(1):89–99. - PubMed
-
- Safaeian M, Ghosh A, Porras C, et al. Direct comparison of HPV16 serological assays used to define HPV-naive women in HPV vaccine trials. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2012;21(9):1547–1554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

