Genetic variation in iron metabolism is associated with neuropathic pain and pain severity in HIV-infected patients on antiretroviral therapy
- PMID: 25144566
- PMCID: PMC4140681
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103123
Genetic variation in iron metabolism is associated with neuropathic pain and pain severity in HIV-infected patients on antiretroviral therapy
Abstract
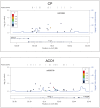
HIV sensory neuropathy and distal neuropathic pain (DNP) are common, disabling complications associated with combination antiretroviral therapy (cART). We previously associated iron-regulatory genetic polymorphisms with a reduced risk of HIV sensory neuropathy during more neurotoxic types of cART. We here evaluated the impact of polymorphisms in 19 iron-regulatory genes on DNP in 560 HIV-infected subjects from a prospective, observational study, who underwent neurological examinations to ascertain peripheral neuropathy and structured interviews to ascertain DNP. Genotype-DNP associations were explored by logistic regression and permutation-based analytical methods. Among 559 evaluable subjects, 331 (59%) developed HIV-SN, and 168 (30%) reported DNP. Fifteen polymorphisms in 8 genes (p<0.05) and 5 variants in 4 genes (p<0.01) were nominally associated with DNP: polymorphisms in TF, TFRC, BMP6, ACO1, SLC11A2, and FXN conferred reduced risk (adjusted odds ratios [ORs] ranging from 0.2 to 0.7, all p<0.05); other variants in TF, CP, ACO1, BMP6, and B2M conferred increased risk (ORs ranging from 1.3 to 3.1, all p<0.05). Risks associated with some variants were statistically significant either in black or white subgroups but were consistent in direction. ACO1 rs2026739 remained significantly associated with DNP in whites (permutation p<0.0001) after correction for multiple tests. Several of the same iron-regulatory-gene polymorphisms, including ACO1 rs2026739, were also associated with severity of DNP (all p<0.05). Common polymorphisms in iron-management genes are associated with DNP and with DNP severity in HIV-infected persons receiving cART. Consistent risk estimates across population subgroups and persistence of the ACO1 rs2026739 association after adjustment for multiple testing suggest that genetic variation in iron-regulation and transport modulates susceptibility to DNP.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Hitchcock SA, Meyer HP, Gwyther E (2008) Neuropathic pain in AIDS patients prior to antiretroviral therapy. S Afr Med J 98: 889–892. - PubMed
-
- Apostolova N, Blas-Garcia A, Esplugues JV (2011) Mitochondrial interference by anti-HIV drugs: mechanisms beyond Pol-gamma inhibition. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 32: 715–725. - PubMed
-
- Hulgan T, Haas DW, Haines JL, Ritchie MD, Robbins GK, et al. (2005) Mitochondrial haplogroups and peripheral neuropathy during antiretroviral therapy: an adult AIDS clinical trials group study. AIDS 19: 1341–1349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

