Extensive translation of small Open Reading Frames revealed by Poly-Ribo-Seq
- PMID: 25144939
- PMCID: PMC4359375
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03528
Extensive translation of small Open Reading Frames revealed by Poly-Ribo-Seq
Abstract
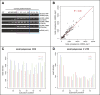
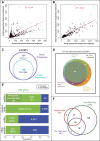
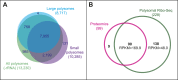
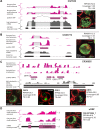
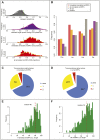
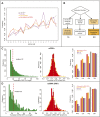
Thousands of small Open Reading Frames (smORFs) with the potential to encode small peptides of fewer than 100 amino acids exist in our genomes. However, the number of smORFs actually translated, and their molecular and functional roles are still unclear. In this study, we present a genome-wide assessment of smORF translation by ribosomal profiling of polysomal fractions in Drosophila. We detect two types of smORFs bound by multiple ribosomes and thus undergoing productive translation. The 'longer' smORFs of around 80 amino acids resemble canonical proteins in translational metrics and conservation, and display a propensity to contain transmembrane motifs. The 'dwarf' smORFs are in general shorter (around 20 amino-acid long), are mostly found in 5'-UTRs and non-coding RNAs, are less well conserved, and have no bioinformatic indicators of peptide function. Our findings indicate that thousands of smORFs are translated in metazoan genomes, reinforcing the idea that smORFs are an abundant and fundamental genome component.
Keywords: biochemistry; d. melanogaster; evolutionary biology; genomics; non-coding RNAs; small open reading Frames; transmembrane peptides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Bazzini AA, Johnstone TG, Christiano R, Mackowiak SD, Obermayer B, Fleming ES, Vejnar CE, Lee MT, Rajewsky N, Walther TC, Giraldez AJ. Identification of small ORFs in vertebrates using ribosome footprinting and evolutionary conservation. The EMBO Journal. 2014;33:981–993. doi: 10.1002/embj.201488411. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

