Controlling gene networks and cell fate with precision-targeted DNA-binding proteins and small-molecule-based genome readers
- PMID: 25145439
- PMCID: PMC4205157
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20140400
Controlling gene networks and cell fate with precision-targeted DNA-binding proteins and small-molecule-based genome readers
Abstract
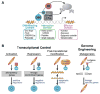
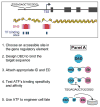
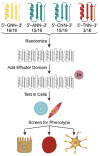
Transcription factors control the fate of a cell by regulating the expression of genes and regulatory networks. Recent successes in inducing pluripotency in terminally differentiated cells as well as directing differentiation with natural transcription factors has lent credence to the efforts that aim to direct cell fate with rationally designed transcription factors. Because DNA-binding factors are modular in design, they can be engineered to target specific genomic sequences and perform pre-programmed regulatory functions upon binding. Such precision-tailored factors can serve as molecular tools to reprogramme or differentiate cells in a targeted manner. Using different types of engineered DNA binders, both regulatory transcriptional controls of gene networks, as well as permanent alteration of genomic content, can be implemented to study cell fate decisions. In the present review, we describe the current state of the art in artificial transcription factor design and the exciting prospect of employing artificial DNA-binding factors to manipulate the transcriptional networks as well as epigenetic landscapes that govern cell fate.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Reprogramming cell fate with a genome-scale library of artificial transcription factors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Dec 20;113(51):E8257-E8266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1611142114. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27930301 Free PMC article.
-
Specificity landscapes of DNA binding molecules elucidate biological function.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Mar 9;107(10):4544-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914023107. Epub 2010 Feb 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20176964 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered zinc finger proteins for controlling stem cell fate.Stem Cells. 2003;21(6):632-7. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.21-6-632. Stem Cells. 2003. PMID: 14595122
-
Polyamides as artificial transcription factors: novel tools for molecular medicine?Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2004 May 3;43(19):2472-5. doi: 10.1002/anie.200301745. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2004. PMID: 15127431 Review. No abstract available.
-
Step out of the groove: epigenetic gene control systems and engineered transcription factors.Adv Genet. 2006;56:163-204. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2660(06)56005-5. Adv Genet. 2006. PMID: 16735158 Review.
Cited by
-
Reprogramming cell fate with artificial transcription factors.FEBS Lett. 2018 Mar;592(6):888-900. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12993. Epub 2018 Feb 11. FEBS Lett. 2018. PMID: 29389011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MYC2: A Master Switch for Plant Physiological Processes and Specialized Metabolite Synthesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 9;24(4):3511. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043511. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleosome distortion as a possible mechanism of transcription activation domain function.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2016 Sep 20;9:40. doi: 10.1186/s13072-016-0092-2. eCollection 2016. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2016. PMID: 27679670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reprogramming cell fate with a genome-scale library of artificial transcription factors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Dec 20;113(51):E8257-E8266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1611142114. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27930301 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide Mapping of Drug-DNA Interactions in Cells with COSMIC (Crosslinking of Small Molecules to Isolate Chromatin).J Vis Exp. 2016 Jan 20;(107):e53510. doi: 10.3791/53510. J Vis Exp. 2016. PMID: 26863565 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663–676. - PubMed
-
- Davis RL, Weintraub H, Lassar AB. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987;51:987–1000. - PubMed
-
- Cohen DE, Melton D. Turning straw into gold: directing cell fate for regenerative medicine. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12:243–252. - PubMed
-
- Graf T, Enver T. Forcing cells to change lineages. Nature. 2009;462:587–594. - PubMed
-
- Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K, Antosiewicz-Bourget J, Frane JL, Tian S, Nie J, Jonsdottir GA, Ruotti V, Stewart R, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science. 2007;318:1917–1920. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

