Controlling gene networks and cell fate with precision-targeted DNA-binding proteins and small-molecule-based genome readers
- PMID: 25145439
- PMCID: PMC4205157
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20140400
Controlling gene networks and cell fate with precision-targeted DNA-binding proteins and small-molecule-based genome readers
Abstract
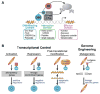
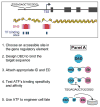
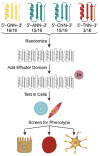
Transcription factors control the fate of a cell by regulating the expression of genes and regulatory networks. Recent successes in inducing pluripotency in terminally differentiated cells as well as directing differentiation with natural transcription factors has lent credence to the efforts that aim to direct cell fate with rationally designed transcription factors. Because DNA-binding factors are modular in design, they can be engineered to target specific genomic sequences and perform pre-programmed regulatory functions upon binding. Such precision-tailored factors can serve as molecular tools to reprogramme or differentiate cells in a targeted manner. Using different types of engineered DNA binders, both regulatory transcriptional controls of gene networks, as well as permanent alteration of genomic content, can be implemented to study cell fate decisions. In the present review, we describe the current state of the art in artificial transcription factor design and the exciting prospect of employing artificial DNA-binding factors to manipulate the transcriptional networks as well as epigenetic landscapes that govern cell fate.
Figures



References
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663–676. - PubMed
-
- Davis RL, Weintraub H, Lassar AB. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987;51:987–1000. - PubMed
-
- Cohen DE, Melton D. Turning straw into gold: directing cell fate for regenerative medicine. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12:243–252. - PubMed
-
- Graf T, Enver T. Forcing cells to change lineages. Nature. 2009;462:587–594. - PubMed
-
- Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K, Antosiewicz-Bourget J, Frane JL, Tian S, Nie J, Jonsdottir GA, Ruotti V, Stewart R, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science. 2007;318:1917–1920. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

