Human lysyl oxidase-like 2
- PMID: 25146937
- PMCID: PMC6309629
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2014.07.003
Human lysyl oxidase-like 2
Abstract
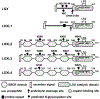
Lysyl oxidase like-2 (LOXL2) belongs to the lysyl oxidase (LOX) family, which comprises Cu(2+)- and lysine tyrosylquinone (LTQ)-dependent amine oxidases. LOXL2 is proposed to function similarly to LOX in the extracellular matrix (ECM) by promoting crosslinking of collagen and elastin. LOXL2 has also been proposed to regulate extracellular and intracellular cell signaling pathways. Dysregulation of LOXL2 has been linked to many diseases, including cancer, pro-oncogenic angiogenesis, fibrosis and heart diseases. In this review, we will give an overview of the current understandings and hypotheses regarding the molecular functions of LOXL2.
Keywords: Cell signaling; Extracellular matrix; Lysine tyrosylquinone (LTQ); Lysyl oxidase family; Lysyl oxidase like-2; Tumor metastasis/invasion.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


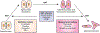





References
-
- Kenyon K, Modi WS, Contente S, and Friedman RM (1993) J Biol Chem 268, 18435–18437 - PubMed
-
- Kim Y, Boyd CD, and Csiszar K (1995) J Biol Chem 270, 7176–7182 - PubMed
-
- Saito H, Papaconstantinou J, Sato H, and Goldstein S (1997) J Biol Chem 272, 8157–8160 - PubMed
-
- Huang Y, Dai J, Tang R, Zhao W, Zhou Z, Wang W, Ying K, Xie Y, and Mao Y (2001) Matrix Biol 20, 153–157 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

