SecureMA: protecting participant privacy in genetic association meta-analysis
- PMID: 25147357
- PMCID: PMC4296153
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu561
SecureMA: protecting participant privacy in genetic association meta-analysis
Abstract
Motivation: Sharing genomic data is crucial to support scientific investigation such as genome-wide association studies. However, recent investigations suggest the privacy of the individual participants in these studies can be compromised, leading to serious concerns and consequences, such as overly restricted access to data.
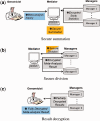
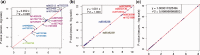
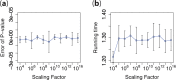
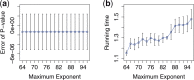
Results: We introduce a novel cryptographic strategy to securely perform meta-analysis for genetic association studies in large consortia. Our methodology is useful for supporting joint studies among disparate data sites, where privacy or confidentiality is of concern. We validate our method using three multisite association studies. Our research shows that genetic associations can be analyzed efficiently and accurately across substudy sites, without leaking information on individual participants and site-level association summaries.
Availability and implementation: Our software for secure meta-analysis of genetic association studies, SecureMA, is publicly available at http://github.com/XieConnect/SecureMA. Our customized secure computation framework is also publicly available at http://github.com/XieConnect/CircuitService.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

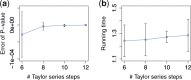
References
-
- Asharov G, et al. Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Computers & Communications Security. 2013. More efficient oblivious transfer and extensions for faster secure computation; pp. 535–548.
-
- Ayday E, et al. Data Privacy Management and Autonomous Spontaneous Security. Springer, Berlin, Germany; 2014. Privacy-preserving processing of raw genomic data; pp. 133–147.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

