Earthworm is a versatile and sustainable biocatalyst for organic synthesis
- PMID: 25148527
- PMCID: PMC4141794
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105284
Earthworm is a versatile and sustainable biocatalyst for organic synthesis
Abstract
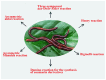
A crude extract of earthworms was used as an eco-friendly, environmentally benign, and easily accessible biocatalyst for various organic synthesis including the asymmetric direct aldol and Mannich reactions, Henry and Biginelli reactions, direct three-component aza-Diels-Alder reactions for the synthesis of isoquinuclidines, and domino reactions for the synthesis of coumarins. Most of these reactions have never before seen in nature, and moderate to good enantioselectivities in aldol and Mannich reactions were obtained with this earthworm catalyst. The products can be obtained in preparatively useful yields, and the procedure does not require any additional cofactors or special equipment. This work provides an example of a practical way to use sustainable catalysts from nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



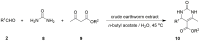

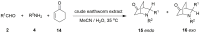
References
-
- Maruoka K, List B, Yamamoto H, Gong LZ (2012) Organocatalysis: a web collection. Chem Commun 48: 10703–10703. - PubMed
-
- Toscano MD, Woycechowsky KJ, Hilvert D (2007) Minimalist active-site redesign: teaching old enzymes new tricks. Angew Chem Int Ed 46: 3212–3236. - PubMed
-
- Arnold FH (2001) Combinatorial and computational challenges for biocatalyst design. Nature 409: 253–257. - PubMed
-
- Bommarius AS, Riebel BR (2004) Biocatalysis: Fundamentals and Applications. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH.
-
- Johannes T, Simurdiak MR, Zhao H (2006) Biocatalysis, Encyclopedia of Chemical Processing. Taylor & Francis. DOI: 10.1081/E-ECHP-120017565.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

