Improved virological and immunological efficacy of resistance-guided switch in antiretroviral therapy: a Frankfurt HIV cohort analysis
- PMID: 25148909
- PMCID: PMC4233158
- DOI: 10.1007/s00430-014-0350-5
Improved virological and immunological efficacy of resistance-guided switch in antiretroviral therapy: a Frankfurt HIV cohort analysis
Abstract
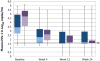
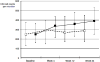
To evaluate the treatment outcome of antiretroviral therapy, depending on the use and utility of a concept of resistance-guided switch, patients from the Frankfurt HIV cohort have been followed for 24 weeks. If available, prior resistance data have been evaluated and patients were grouped into their expected viral response. The data of 354 patients were thus analysed, taking into account the genotypic sensitivity score of the administered medication (> or ≤2). When looking at the proportion of patients who achieved a viral load of <50/ml, the response rates differed significantly better for patients with a favourable resistance scoring as compared to an unfavourable one (71.9 % as compared to 56.0 %, p = 0.008). Interestingly, patients with a favourable resistance score also showed a better immunological response, as measured by median CD4 cell count of 391/µl [interquartal range (IQR) 250-530/µl] against 287/µl (IQR 174-449/µl) and a larger total increase of 141/µl against 38/µl. A significant virological and immunological benefit could be demonstrated for patients of a cohort with resistance-guided antiretroviral therapy adjustments.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: All authors have declared no further conflict of interest, related to this article.
Figures

References
-
- Palella FJ, Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, Loveless MO, Fuhrer J, Satten GA, Aschman DJ, Holmberg SD. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV outpatient study investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–860. - PubMed
-
- Yazdanpanah Y, Fagard C, Descamps D, Taburet AM, Colin C, Roquebert B, Katlama C, Pialoux G, Jacomet C, Piketty C, Bollens D, Molina JM, Chêne G ANRS 139 TRIO Trial Group. High rate of virologic suppression with raltegravir plus etravirine and darunavir/ritonavir among treatment-experienced patients infected with multidrug-resistant HIV: results of the ANRS 139 TRIO trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49:1441–1449. - PubMed
-
- Imaz A, del Saz SV, Ribas MA, Curran A, Caballero E, Falcó V, Crespo M, Ocaña I, Diaz M, de Gopegui ER, Riera M, Ribera E. Raltegravir, etravirine, and ritonavir-boosted darunavir: a safe and successful rescue regimen for multidrug-resistant HIV-1 infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2009;52:382–386. - PubMed
-
- Gulick RM, Lalezari J, Goodrich J, Clumeck N, DeJesus E, Horban A, Nadler J, Clotet B, Karlsson A, Wohlfeiler M, Montana JB, McHale M, Sullivan J, Ridgway C, Felstead S, Dunne MW, van der Ryst E, Mayer H MOTIVATE study teams. Maraviroc for previously treated patients with R5 HIV-1 infection. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1429–1441. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fätkenheuer G, Nelson M, Lazzarin A, Konourina I, Hoepelman AI, Lampiris H, Hirschel B, Tebas P, Raffi F, Trottier B, Bellos N, Saag M, Cooper DA, Westby M, Tawadros M, Sullivan JF, Ridgway C, Dunne MW, Felstead S, Mayer H, van der Ryst E MOTIVATE 1 and MOTIVATE 2 study teams. Subgroup analyses of maraviroc in previously treated R5 HIV-1 infection. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1442–1455. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

