Examining the critical roles of human CB2 receptor residues Valine 3.32 (113) and Leucine 5.41 (192) in ligand recognition and downstream signaling activities
- PMID: 25148941
- PMCID: PMC4465889
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.08.048
Examining the critical roles of human CB2 receptor residues Valine 3.32 (113) and Leucine 5.41 (192) in ligand recognition and downstream signaling activities
Abstract
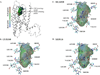
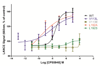
We performed molecular modeling and docking to predict a putative binding pocket and associated ligand-receptor interactions for human cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2). Our data showed that two hydrophobic residues came in close contact with three structurally distinct CB2 ligands: CP-55,940, SR144528 and XIE95-26. Site-directed mutagenesis experiments and subsequent functional assays implicated the roles of Valine residue at position 3.32 (V113) and Leucine residue at position 5.41 (L192) in the ligand binding function and downstream signaling activities of the CB2 receptor. Four different point mutations were introduced to the wild type CB2 receptor: V113E, V113L, L192S and L192A. Our results showed that mutation of Val113 with a Glutamic acid and Leu192 with a Serine led to the complete loss of CB2 ligand binding as well as downstream signaling activities. Substitution of these residues with those that have similar hydrophobic side chains such as Leucine (V113L) and Alanine (L192A), however, allowed CB2 to retain both its ligand binding and signaling functions. Our modeling results validated by competition binding and site-directed mutagenesis experiments suggest that residues V113 and L192 play important roles in ligand binding and downstream signaling transduction of the CB2 receptor.
Keywords: Adenylyl cyclase (AC activity); Cannabinoid receptor subtype 2 (CB2); Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP); Molecular modeling; Site-directed mutagenesis; Time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy (TR-FRET) transfer.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures


References
-
- Matsuda LA, Lolait SJ, Brownstein MJ, Young AC, Bonner TI. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature. 1990;346:561. - PubMed
-
- Munro S, Thomas KL, Abu-Shaar M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature. 1993;365:61. - PubMed
-
- Racz I, Nadal X, Alferink J, Banos JE, Rehnelt J, Martin M, et al. Crucial role of CB(2) cannabinoid receptor in the regulation of central immune responses during neuropathic pain. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 2008;28:12125–12135. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

