Functional importance of cardiac enhancer-associated noncoding RNAs in heart development and disease
- PMID: 25149110
- PMCID: PMC4445080
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.08.009
Functional importance of cardiac enhancer-associated noncoding RNAs in heart development and disease
Abstract
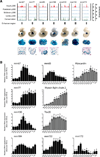
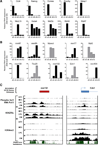
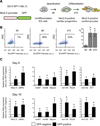
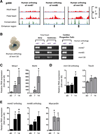
The key information processing units within gene regulatory networks are enhancers. Enhancer activity is associated with the production of tissue-specific noncoding RNAs, yet the existence of such transcripts during cardiac development has not been established. Using an integrated genomic approach, we demonstrate that fetal cardiac enhancers generate long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) during cardiac differentiation and morphogenesis. Enhancer expression correlates with the emergence of active enhancer chromatin states, the initiation of RNA polymerase II at enhancer loci and expression of target genes. Orthologous human sequences are also transcribed in fetal human hearts and cardiac progenitor cells. Through a systematic bioinformatic analysis, we identified and characterized, for the first time, a catalog of lncRNAs that are expressed during embryonic stem cell differentiation into cardiomyocytes and associated with active cardiac enhancer sequences. RNA-sequencing demonstrates that many of these transcripts are polyadenylated, multi-exonic long noncoding RNAs. Moreover, knockdown of two enhancer-associated lncRNAs resulted in the specific downregulation of their predicted target genes. Interestingly, the reactivation of the fetal gene program, a hallmark of the stress response in the adult heart, is accompanied by increased expression of fetal cardiac enhancer transcripts. Altogether, these findings demonstrate that the activity of cardiac enhancers and expression of their target genes are associated with the production of enhancer-derived lncRNAs.
Keywords: Cardiac development; Enhancers; Gene regulation; Gene regulatory networks; Heart failure; Long noncoding RNA (lncRNAs).
Copyright © 2014. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
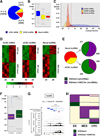
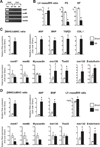
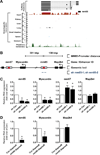
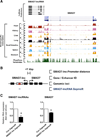
Comment in
-
Non-coding RNA enhances cardiac development.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 Nov;76:205-7. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.09.005. Epub 2014 Sep 18. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 25240640 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

