Chronic alcohol exposure differentially affects activation of female locus coeruleus neurons and the subcellular distribution of corticotropin releasing factor receptors
- PMID: 25149913
- PMCID: PMC4258542
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.08.005
Chronic alcohol exposure differentially affects activation of female locus coeruleus neurons and the subcellular distribution of corticotropin releasing factor receptors
Abstract
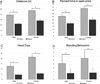
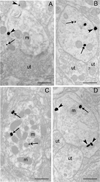
Understanding the neurobiological bases for sex differences in alcohol dependence is needed to help guide the development of individualized therapies for alcohol abuse disorders. In the present study, alcohol-induced adaptations in (1) anxiety-like behavior, (2) patterns of c-Fos activation and (3) subcellular distribution of corticotropin releasing factor receptor in locus coeruleus (LC) neurons was investigated in male and female Sprague-Dawley rats that were chronically exposed to ethanol using a liquid diet. Results confirm and extend reports by others showing that chronic ethanol exposure produces an anxiogenic-like response in both male and female subjects. Ethanol-induced sex differences were observed with increased c-Fos expression in LC neurons of female ethanol-treated subjects compared to controls or male subjects. Results also reveal sex differences in the subcellular distribution of the CRFr in LC-noradrenergic neurons with female subjects exposed to ethanol exhibiting a higher frequency of plasmalemmal CRFrs. These adaptations have implications for LC neuronal activity and its neural targets across the sexes. Considering the important role of the LC in ethanol-induced activation of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, the present results indicate important sex differences in feed-forward regulation of the HPA axis that may render alcohol dependent females more vulnerable to subsequent stress exposure.
Keywords: CRFr; Chronic alcohol; Locus coeruleus; Sex differences; c-Fos.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Baldwin HA, Rassnick S, Rivier J, Koob GF, Britton KT. CRF antagonist reverses the "anxiogenic" response to ethanol withdrawal in the rat. Psychopharmacology. 1991;103(2):227–232. - PubMed
-
- Bangasser DA, Curtis A, Reyes BA, Bethea TT, Parastatidis I, Ischiropoulos H, Van Bockstaele EJ, Valentino RJ. Sex differences in corticotropin-releasing factor receptor signaling and trafficking: potential role in female vulnerability to stress-related psychopathology. Mol Psychiatry. 2010a;15(9):877, 896–904. doi:mp201066 [pii] 10.1038/mp.2010.66. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bangasser DA, Curtis A, Reyes BA, Bethea TT, Parastatidis I, Ischiropoulos H, Van Bockstaele EJ, Valentino RJ. Sex differences in corticotropin-releasing factor receptor signaling and trafficking: potential role in female vulnerability to stress-related psychopathology. Molecular psychiatry. 2010b;15(9):877, 896–904. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

