Hyperinfection strongyloidiasis in renal transplant recipients
- PMID: 25150235
- PMCID: PMC4154012
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2014-205068
Hyperinfection strongyloidiasis in renal transplant recipients
Abstract
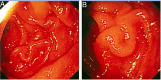
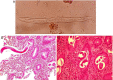
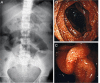
Strongyloidiasis is infection caused by the nematode Strongyloides stercoralis. Chronic uncomplicated strongyloidiasis is known to occur in immunocompetent individuals while hyperinfection and dissemination occurs in selective immunosuppressed hosts particularly those on corticosteroid therapy. We report two cases of hyperinfection strongyloidiasis in renal transplant recipients and document endoscopic and pathological changes in the involved small bowel. One patient presented with features of dehydration and malnutrition while another developed ileal obstruction and strangulation, requiring bowel resection. Oesophagogastroduodenoscopy showed erythematous and thickened duodenal mucosal folds. Histopathological examination of duodenal biopsies revealed S. stercoralis worms, larvae and eggs embedded in mucosa and submucosa. Wet mount stool preparation showed filariform larvae of S. stercoralis in both cases. Patients were managed with anthelmintic therapy (ivermectin/albendazole) and concurrent reduction of immunosuppression. Both patients had uneventful recovery. Complicated strongyloidiasis should be suspected in immunocompromised hosts who present with abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhoea, particularly in endemic areas.
2014 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Segarra-Newnham M. Manifestations, diagnosis and treatment of Strongyloides stercoralis infection. Ann Pharmacother 2007;41:1992. - PubMed
-
- Siddiqui AA, Genta RM, Maguilnik I, et al. Strongyloidiasis. In: Guerrant RL, Walker DH, Weller PF, eds Tropical infectious siseases: principles, pathogens & practice. Philadelphia: Saunders, 2011:805–12
-
- Genta RM. Immunobiology of strongyloidiasis. Trop Geogr Med 1984; 36:223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
