Asymmetric mRNA localization contributes to fidelity and sensitivity of spatially localized systems
- PMID: 25150862
- PMCID: PMC4167633
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2876
Asymmetric mRNA localization contributes to fidelity and sensitivity of spatially localized systems
Abstract
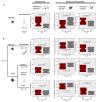
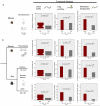
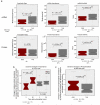
Although many proteins are localized after translation, asymmetric protein distribution is also achieved by translation after mRNA localization. Why are certain mRNA transported to a distal location and translated on-site? Here we undertake a systematic, genome-scale study of asymmetrically distributed protein and mRNA in mammalian cells. Our findings suggest that asymmetric protein distribution by mRNA localization enhances interaction fidelity and signaling sensitivity. Proteins synthesized at distal locations frequently contain intrinsically disordered segments. These regions are generally rich in assembly-promoting modules and are often regulated by post-translational modifications. Such proteins are tightly regulated but display distinct temporal dynamics upon stimulation with growth factors. Thus, proteins synthesized on-site may rapidly alter proteome composition and act as dynamically regulated scaffolds to promote the formation of reversible cellular assemblies. Our observations are consistent across multiple mammalian species, cell types and developmental stages, suggesting that localized translation is a recurring feature of cell signaling and regulation.
Figures


References
-
- Ephrussi A, Dickinson LK, Lehmann R. Oskar organizes the germ plasm and directs localization of the posterior determinant nanos. Cell. 1991;66:37–50. - PubMed
Reference for Online Methods
-
- Han TW, et al. Cell-free formation of RNA granules: bound RNAs identify features and components of cellular assemblies. Cell. 2012;149:768–779. - PubMed
-
- Schwanhausser B, et al. Corrigendum: Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control. Nature. 2013;495:126–127. - PubMed
-
- Dennis GJ, et al. DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 2003;4:P3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

