Microparticles: new light shed on the understanding of venous thromboembolism
- PMID: 25152025
- PMCID: PMC4155535
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2014.73
Microparticles: new light shed on the understanding of venous thromboembolism
Abstract
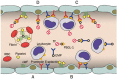
Microparticles are small membrane fragments shed primarily from blood and endothelial cells during either activation or apoptosis. There is mounting evidence suggesting that microparticles perform a large array of biological functions and contribute to various diseases. Of these disease processes, a significant link has been established between microparticles and venous thromboembolism. Advances in research on the role of microparticles in thrombosis have yielded crucial insights into possible mechanisms, diagnoses and therapeutic targets of venous thromboembolism. In this review, we discuss the definition and properties of microparticles and venous thromboembolism, provide a synopsis of the evidence detailing the contributions of microparticles to venous thromboembolism, and propose potential mechanisms, by which venous thromboembolism occurs. Moreover, we illustrate a possible role of microparticles in cancer-related venous thromboembolism.
Figures
References
-
- Ahn YS. Cell-derived microparticles: Miniature envoys with many faces. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3:884–7. - PubMed
-
- Bonderman D, Teml A, Jakowitsch J, Adlbrecht C, Gyöngyösi M, Sperker W, et al. Coronary no-reflow is caused by shedding of active tissue factor from dissected atherosclerotic plaque. Blood. 2002;99:2794–800. - PubMed
-
- Leroyer AS, Isobe H, Lesèche G, Castier Y, Wassef M, Mallat Z, et al. Cellular origins and thrombogenic activity of microparticles isolated from human atherosclerotic plaques. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;49:772–7. - PubMed
-
- Preston RA, Jy W, Jimenez JJ, Mauro LM, Horstman LL, Valle M, et al. Effects of severe hypertension on endothelial and platelet microparticles. Hypertension. 2003;41:211–7. - PubMed
-
- Sabatier F, Darmon P, Hugel B, Combes V, Sanmarco M, Velut JG, et al. Type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients display different patterns of cellular microparticles. Diabetes. 2002;51:2840–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

