Neu-Laxova syndrome is a heterogeneous metabolic disorder caused by defects in enzymes of the L-serine biosynthesis pathway
- PMID: 25152457
- PMCID: PMC4157144
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.07.012
Neu-Laxova syndrome is a heterogeneous metabolic disorder caused by defects in enzymes of the L-serine biosynthesis pathway
Abstract
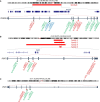
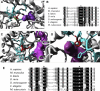
Neu-Laxova syndrome (NLS) is a rare autosomal-recessive disorder characterized by a recognizable pattern of severe malformations leading to prenatal or early postnatal lethality. Homozygous mutations in PHGDH, a gene involved in the first and limiting step in L-serine biosynthesis, were recently identified as the cause of the disease in three families. By studying a cohort of 12 unrelated families affected by NLS, we provide evidence that NLS is genetically heterogeneous and can be caused by mutations in all three genes encoding enzymes of the L-serine biosynthesis pathway. Consistent with recently reported findings, we could identify PHGDH missense mutations in three unrelated families of our cohort. Furthermore, we mapped an overlapping homozygous chromosome 9 region containing PSAT1 in four consanguineous families. This gene encodes phosphoserine aminotransferase, the enzyme for the second step in L-serine biosynthesis. We identified six families with three different missense and frameshift PSAT1 mutations fully segregating with the disease. In another family, we discovered a homozygous frameshift mutation in PSPH, the gene encoding phosphoserine phosphatase, which catalyzes the last step of L-serine biosynthesis. Interestingly, all three identified genes have been previously implicated in serine-deficiency disorders, characterized by variable neurological manifestations. Our findings expand our understanding of NLS as a disorder of the L-serine biosynthesis pathway and suggest that NLS represents the severe end of serine-deficiency disorders, demonstrating that certain complex syndromes characterized by early lethality could indeed be the extreme end of the phenotypic spectrum of already known disorders.
Copyright © 2014 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Neu R.L., Kajii T., Gardner L.I., Nagyfy S.F. A lethal syndrome of microcephaly with multiple congenital anomalies in three siblings. Pediatrics. 1971;47:610–612. - PubMed
-
- Laxova R., Ohara P.T., Timothy J.A. A further example of a lethal autosomal recessive condition in sibs. J. Ment. Defic. Res. 1972;16:139–143. - PubMed
-
- Manning M.A., Cunniff C.M., Colby C.E., El-Sayed Y.Y., Hoyme H.E. Neu-Laxova syndrome: detailed prenatal diagnostic and post-mortem findings and literature review. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2004;125A:240–249. - PubMed
-
- Tabatabaie L., de Koning T.J., Geboers A.J., van den Berg I.E., Berger R., Klomp L.W. Novel mutations in 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PHGDH) are distributed throughout the protein and result in altered enzyme kinetics. Hum. Mutat. 2009;30:749–756. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

