Measuring the safety of excreta disposal behavior in India with the new Safe San Index: reliability, validity and utility
- PMID: 25153464
- PMCID: PMC4143864
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph110808319
Measuring the safety of excreta disposal behavior in India with the new Safe San Index: reliability, validity and utility
Abstract
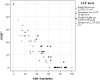
Methods to assess household excreta disposal practices are critical for informing public health outcomes of efforts to improve sanitation in developing countries. We present a new metric, the Safe San Index (SSI), to quantify the hygienic safety of a household's defecation and human feces disposal practices in India, where behavioral outcomes from on-going public expenditures to construct household sanitation facilities and eliminate open defecation are poorly measured. We define hygienic safety of feces disposal as capture in a hygienic sanitation facility. The SSI consists of 15 self-report items and two sub-scales, Latrine Use Frequency and Seven-Day Open Defecation Rate. Households are scored on a standardized scale from 0 (no defecation safely captured) to 100 (all defecation safely captured). We present results of a pilot study in Odisha, India to apply the Index to assess excreta disposal behaviors among rural households and evaluate the reliability and validity of the Index for estimating the rate of correct and consistent sanitation facility usage of household with an improved latrine.
Figures


References
-
- WSP . Economic Impacts of Inadequate Sanitation in India. Water and Sanitation Program. World Bank; New Delhi, India: 2010. [(accessed on 1 February 2014)]. Available online: http://www.wsp.org/sites/wsp.org/files/publications/wsp-esi-india.pdf.
-
- Government of India Total Sanitation Campaign and Nirmal Gram Puraskar Websites, Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation. [(accessed on 3 March 2014)];2014 Available online: http://tsc.gov.in/nbadashboard and http://nirmalgrampuraskar.nic.in/
-
- Banda K., Sarkar R., Gopal S., Govindarajan J., Harijan B.B., Jeyakumar M.B., Mitta P., Sadanala M.E., Selwyn T., Suresh C.R., et al. Water handling, sanitation and defecation practices in rural southern India: A knowledge, attitudes and practices study. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007;101:1124–1130. doi: 10.1016/j.trstmh.2007.05.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Murugesan A., Vikram A., Dayal V., Chugh S. An empirical study of sanitation and health in rural Uttarakhand, India. IJEES. 2008;10:91–99.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

