Role of Bcl-xL/Beclin-1 in synergistic apoptotic effects of secretory TRAIL-armed adenovirus in combination with mitomycin C and hyperthermia on colon cancer cells
- PMID: 25156145
- PMCID: PMC4196052
- DOI: 10.1007/s10495-014-1028-6
Role of Bcl-xL/Beclin-1 in synergistic apoptotic effects of secretory TRAIL-armed adenovirus in combination with mitomycin C and hyperthermia on colon cancer cells
Abstract
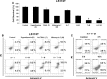
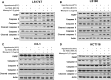
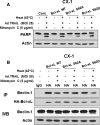
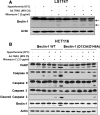
In this study, we attempted to develop a multimodality approach using chemotherapeutic agent mitomycin C, biologic agent tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL/Apo-2L), and mild hyperthermia to treat colon cancer. For this study, human colon cancer LS174T, LS180, HCT116 and CX-1 cells were infected with secretory TRAIL-armed adenovirus (Ad.TRAIL) and treated with chemotherapeutic agent mitomycin C and hyperthermia. The combinatorial treatment caused a synergistic induction of apoptosis which was mediated through an increase in caspase activation. The combinational treatment promoted the JNK-Bcl-xL-Bak pathway which transmitted the synergistic effect through the mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway. JNK signaling led to Bcl-xL phosphorylation at serine 62, dissociation of Bak from Bcl-xL, oligomerization of Bak, alteration of mitochondrial membrane potential, and subsequent cytochrome c release. Overexpression of dominant-negative mutant of Bcl-xL (S62A), but not dominant-positive mutant of Bcl-xL (S62D), suppressed the synergistic death effect. Interestingly, Beclin-1 was dissociated from Bcl-xL and overexpression of dominant-negative mutant of Bcl-xL (S62A), but not dominant-positive mutant of Bcl-xL (S62D), suppressed dissociation of Beclin-1 from Bcl-xL. A combinatorial treatment of mitomycin C, Ad.TRAIL and hyperthermia induced Beclin-1 cleavage, but the Beclin-1 cleavage was abolished in Beclin-1 double mutant (D133A/D146A) knock-in HCT116 cells, suppressing the apoptosis induced by the combination therapy. We believe that this study supports the application of the multimodality approach to colon cancer therapy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of Bcl-xL/Beclin-1 in interplay between apoptosis and autophagy in oxaliplatin and bortezomib-induced cell death.Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Mar 15;88(2):178-88. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2014.01.027. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24486574 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Bcl-xL in synergistic induction of apoptosis by mapatumumab and oxaliplatin in combination with hyperthermia on human colon cancer.Mol Cancer Res. 2012 Dec;10(12):1567-79. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0209-T. Epub 2012 Oct 10. Mol Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 23051936 Free PMC article.
-
Oxaliplatin sensitizes human colon cancer cells to TRAIL through JNK-dependent phosphorylation of Bcl-xL.Gastroenterology. 2011 Aug;141(2):663-73. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.04.055. Epub 2011 Apr 30. Gastroenterology. 2011. PMID: 21683075
-
Impaired autophagy and APP processing in Alzheimer's disease: The potential role of Beclin 1 interactome.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Jul-Aug;106-107:33-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23827971 Review.
-
The Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis.Cell Death Differ. 2011 Apr;18(4):571-80. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.191. Epub 2011 Feb 11. Cell Death Differ. 2011. PMID: 21311563 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of Oncogenic Transcription Factor REL by the Natural Product Derivative Calafianin Monomer 101 Induces Proliferation Arrest and Apoptosis in Human B-Lymphoma Cell Lines.Molecules. 2015 Apr 23;20(5):7474-94. doi: 10.3390/molecules20057474. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25915462 Free PMC article.
-
Developing TRAIL/TRAIL death receptor-based cancer therapies.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018 Dec;37(4):733-748. doi: 10.1007/s10555-018-9728-y. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018. PMID: 29541897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperthermia exposure induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation in HCT116 cells by upregulating miR-34a and causing transcriptional activation of p53.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Dec;14(6):5379-5386. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5257. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 29285066 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperthermia Treatment as a Promising Anti-Cancer Strategy: Therapeutic Targets, Perspective Mechanisms and Synergistic Combinations in Experimental Approaches.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Mar 24;11(4):625. doi: 10.3390/antiox11040625. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Theaflavin-3, 3'-digallate induces apoptosis and G2 cell cycle arrest through the Akt/MDM2/p53 pathway in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer A2780/CP70 cells.Int J Oncol. 2016 Jun;48(6):2657-65. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3472. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27082635 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saltz LB, Cox JV, Blanke C, Rosen LS, Fehrenbacher L, Moore MJ, Maroun JA, Ackland SP, Locker PK, Pirotta N, Elfring GL, Miller LL. Irinotecan plus fluorouracil and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. Irinotecan Study Group. N Eng J Med. 2000;343:905–914. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200009283431302. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, Berlin J, Baron A, Griffing S, Holmgren E, Ferrara N, Fyfe G, Rogers B, Ross R, Kabbinavar F. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2335–2342. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa032691. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Colucci G, Gebbia V, Paoletti G, Giuliani F, Caruso M, Gebbia N, Cartenì G, Agostara B, Pezzella G, Manzione L, Borsellino N, Misino A, Romito S, Durini E, Cordio S, Di Seri M, Lopez M, Maiello E, Montemurro S, Cramarossa A, Lorusso V, Di Bisceglie M, Chiarenza M, Valerio MR, Guida T, Leonardi V, Pisconti S, Rosati G, Carrozza F, Nettis G, Valdesi M, Filippelli G, Fortunato S, Mancarella S, Brunetti C. Phase III randomized trial of FOLFIRI versus FOLFOX4 in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: a multicenter study of the Gruppo Oncologico Dell’Italia Meridionale. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:4866–4875. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.07.113. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cassidy J, Clarke S, Díaz-Rubio E, Scheithauer W, Figer A, Wong R, Koski S, Lichinitser M, Yang TS, Rivera F, Couture F, Sirzén F, Saltz L. Randomized phase III study of capecitabine plus oxaliplatin compared with fluorouracil/folinic acid plus oxaliplatin as first-line therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2006–2012. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.14.9898. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

