Position and length of fatty acids strongly affect receptor selectivity pattern of human pancreatic polypeptide analogues
- PMID: 25156249
- PMCID: PMC5518309
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201402235
Position and length of fatty acids strongly affect receptor selectivity pattern of human pancreatic polypeptide analogues
Abstract
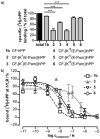
Pancreatic polypeptide (PP) is a satiety-inducing gut hormone targeting predominantly the Y4 receptor within the neuropeptide Y multiligand/multireceptor family. Palmitoylated PP-based ligands have already been reported to exert prolonged satiety-inducing effects in animal models. Here, we suggest that other lipidation sites and different fatty acid chain lengths may affect receptor selectivity and metabolic stability. Activity tests revealed significantly enhanced potency of long fatty acid conjugates on all four Y receptors with a preference of position 22 over 30 at Y1 , Y2 and Y5 receptors. Improved Y receptor selectivity was observed for two short fatty acid analogues. Moreover, [K(30)(E-Prop)]hPP2-36 (15) displayed enhanced stability in blood plasma and liver homogenates. Thus, short chain lipidation of hPP at key residue 30 is a promising approach for anti-obesity therapy because of maintained selectivity and a sixfold increased plasma half-life.
Keywords: lipidation; pancreatic polypeptide; receptors; selectivity; therapeutic peptides.
© 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Pancreatic polypeptide is recognized by two hydrophobic domains of the human Y4 receptor binding pocket.J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 28;289(9):5846-59. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.502021. Epub 2013 Dec 27. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24375409 Free PMC article.
-
Chicken neuropeptide Y-family receptor Y4: a receptor with equal affinity for pancreatic polypeptide, neuropeptide Y and peptide YY.J Mol Endocrinol. 2002 Jun;28(3):225-35. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0280225. J Mol Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 12063188
-
Structural diversity of receptors for neuropeptide Y, peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide.Regul Pept. 1996 Sep 16;65(3):165-74. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(96)00110-3. Regul Pept. 1996. PMID: 8897639 Review.
-
Y-receptor affinity modulation by the design of pancreatic polypeptide/neuropeptide Y chimera led to Y(5)-receptor ligands with picomolar affinity.Peptides. 2001 Mar;22(3):365-78. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(01)00339-4. Peptides. 2001. PMID: 11287091
-
Molecular ligand-receptor interaction of the NPY/PP peptide family.EXS. 2006;(95):35-62. doi: 10.1007/3-7643-7417-9_3. EXS. 2006. PMID: 16382996 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Discovery and Characterization of VU0529331, a Synthetic Small-Molecule Activator of Homomeric G Protein-Gated, Inwardly Rectifying, Potassium (GIRK) Channels.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019 Jan 16;10(1):358-370. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00287. Epub 2018 Sep 13. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30136838 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of fatty diacid acylation of human PYY3-36 on Y2 receptor potency and half-life in minipigs.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 27;11(1):21179. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00654-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34707178 Free PMC article.
-
High molecular weight PEGylation of human pancreatic polypeptide at position 22 improves stability and reduces food intake in mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Nov;173(22):3208-3221. doi: 10.1111/bph.13582. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27545829 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of the Second Extracellular Loop Control Transducer Coupling of Peptide-Activated GPCRs.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 30;24(15):12197. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512197. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569573 Free PMC article.
-
Novel enzyme-resistant pancreatic polypeptide analogs evoke pancreatic beta-cell rest, enhance islet cell turnover, and inhibit food intake in mice.Biofactors. 2024 Nov-Dec;50(6):1101-1112. doi: 10.1002/biof.2059. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Biofactors. 2024. PMID: 38635341 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bard JA, Walker MW, Branchek TA, Weinshank RL. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:26762–26765. - PubMed
-
- Asakawa A, Inui A, Ueno N, Fujimiya M, Fujino MA, Kasuga M. Peptides. 1999;20:1445–1448. - PubMed
-
- Asakawa A, Inui A, Yuzuriha H, Ueno N, Katsuura G, Fujimiya M, Fujino MA, Niijima A, Meguid MM, Kasuga M. Gastroenterology. 2003;124:1325–1336. - PubMed
- Batterham RL, Le Roux CW, Cohen MA, Park AJ, Ellis SM, Patterson M, Frost GS, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:3989–3992. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

