Differential regulation of proinflammatory cytokine expression by mitogen-activated protein kinases in macrophages in response to intestinal parasite infection
- PMID: 25156742
- PMCID: PMC4249314
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.02279-14
Differential regulation of proinflammatory cytokine expression by mitogen-activated protein kinases in macrophages in response to intestinal parasite infection
Abstract
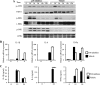
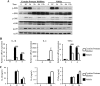
Blastocystis is a common enteric protistan parasite that can cause acute, as well as chronic, infection and is associated with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). However, the pathogenic status of Blastocystis infection remains unclear. In this study, we found that Blastocystis antigens induced abundant expression of proinflammatory cytokines, including interleukin 1β (IL-1β), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), in mouse intestinal explants, in mouse colitis colon, and in macrophages. Further investigation utilizing RAW264.7 murine macrophages showed that Blastocystis treatment in RAW264.7 macrophages induced the activation of ERK, JNK, and p38, the three major groups of mammalian mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases that play essential roles in the expression of proinflammatory cytokines. ERK inhibition in macrophages significantly suppressed both mRNA and protein expression of IL-6 and TNF-α and mRNA expression of IL-1β. On the other hand, JNK inhibition resulted in reductions in both c-Jun and ERK activation and significant suppression of all three proinflammatory cytokines at both the mRNA and protein levels. Inhibition of p38 suppressed only IL-6 protein expression with no effect on the expression of IL-1β and TNF-α. Furthermore, we found that serine proteases produced by Blastocystis play an important role in the induction of ERK activation and proinflammatory cytokine expression by macrophages. Our study thus demonstrated for the first time that Blastocystis could induce the expression of various proinflammatory cytokines via the activation of MAP kinases and that infection with Blastocystis may contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammatory intestinal diseases through the activation of inflammatory pathways in host immune cells, such as macrophages.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β expression pathway induced by Streptococcus mutans in macrophage cell line RAW 264.7.Mol Oral Microbiol. 2012 Jun;27(3):149-59. doi: 10.1111/j.2041-1014.2012.00639.x. Epub 2012 Feb 9. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22520385
-
Administration of ricin induces a severe inflammatory response via nonredundant stimulation of ERK, JNK, and P38 MAPK and provides a mouse model of hemolytic uremic syndrome.Am J Pathol. 2005 Jan;166(1):323-39. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62256-0. Am J Pathol. 2005. PMID: 15632024 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine-stimulated inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in astroglia: role of Erk mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-kappaB.Glia. 2003 Jan 15;41(2):152-60. doi: 10.1002/glia.10168. Glia. 2003. PMID: 12509805
-
Pathogenic mechanisms in Blastocystis spp. - Interpreting results from in vitro and in vivo studies.Parasitol Int. 2016 Dec;65(6 Pt B):772-779. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2016.05.007. Epub 2016 May 13. Parasitol Int. 2016. PMID: 27181702 Review.
-
New insights into the interactions between Blastocystis, the gut microbiota, and host immunity.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Feb 25;17(2):e1009253. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009253. eCollection 2021 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33630979 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Highly Selective In Vitro JNK3 Inhibitor, FMU200, Restores Mitochondrial Membrane Potential and Reduces Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in SH-SY5Y Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 2;22(7):3701. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073701. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33918172 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of Blastocystis in gut microbiota is associated with cognitive traits and decreased executive function.ISME J. 2022 Sep;16(9):2181-2197. doi: 10.1038/s41396-022-01262-3. Epub 2022 Jun 21. ISME J. 2022. PMID: 35729225 Free PMC article.
-
RIPK3 promoter hypermethylation in hepatocytes protects from bile acid-induced inflammation and necroptosis.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Apr 18;14(4):275. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05794-0. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37072399 Free PMC article.
-
Didox (3,4-dihydroxybenzohydroxamic acid) suppresses IL-33-induced cytokine production in primary mouse mast cells.Cell Immunol. 2017 Sep;319:10-16. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2017.04.013. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Cell Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28750923 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of apoptotic responses in Blastocystis sp. upon treatment with Tongkat Ali and Metronidazole.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 9;11(1):7833. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81418-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33837230 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

