Distinct roles for mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and CALMODULIN-BINDING TRANSCRIPTIONAL ACTIVATOR3 in regulating the peak time and amplitude of the plant general stress response
- PMID: 25157030
- PMCID: PMC4213123
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.114.245944
Distinct roles for mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and CALMODULIN-BINDING TRANSCRIPTIONAL ACTIVATOR3 in regulating the peak time and amplitude of the plant general stress response
Abstract
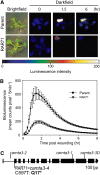
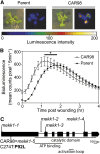
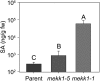
To survive environmental challenges, plants have evolved tightly regulated response networks, including a rapid and transient general stress response (GSR), followed by well-studied stress-specific responses. The mechanisms underpinning the GSR have remained elusive, but a functional cis-element, the rapid stress response element (RSRE), is known to confer transcription of GSR genes rapidly (5 min) and transiently (peaking 90-120 min after stress) in vivo. To investigate signal transduction events in the GSR, we used a 4xRSRE:LUCIFERASE reporter in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), employing complementary approaches of forward and chemical genetic screens, and identified components regulating peak time versus amplitude of RSRE activity. Specifically, we identified a mutant in CALMODULIN-BINDING TRANSCRIPTIONAL ACTIVATOR3 (CAMTA3) with reduced RSRE activation, verifying this transcription factor's role in activation of the RSRE-mediated GSR. Furthermore, we isolated a mutant in MITOGEN-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE (MAPK) KINASE KINASE1 (mekk1-5), which displays increased basal and an approximately 60-min earlier peak of wound-induced RSRE activation. The double mekk1/camta3 mutant positioned CAMTA3 downstream of MEKK1 and verified their distinct roles in GSR regulation. mekk1-5 displays programmed cell death and overaccumulates reactive oxygen species and salicylic acid, hallmarks of the hypersensitive response, suggesting that the hypersensitive response may play a role in the RSRE phenotype in this mutant. In addition, chemical inhibition studies suggest that the MAPK network is required for the rapid peak of the RSRE response, distinguishing the impact of chronic (mekk1-5) from transient (chemical inhibition) loss of MAPK signaling. Collectively, these results reveal underlying regulatory components of the plant GSR and further define their distinct roles in the regulation of this key biological process.
© 2014 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A key general stress response motif is regulated non-uniformly by CAMTA transcription factors.Plant J. 2014 Oct;80(1):82-92. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12620. Epub 2014 Aug 19. Plant J. 2014. PMID: 25039701 Free PMC article.
-
ORA47 is a transcriptional regulator of a general stress response hub.Plant J. 2022 Apr;110(2):562-571. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15688. Epub 2022 Feb 24. Plant J. 2022. PMID: 35092704
-
Plastidial metabolite MEcPP induces a transcriptionally centered stress-response hub via the transcription factor CAMTA3.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Aug 2;113(31):8855-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1602582113. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27432993 Free PMC article.
-
Wiring diagrams of MAPK regulation by MEKK1, 2, and 3.Biochem Cell Biol. 2004 Dec;82(6):658-63. doi: 10.1139/o04-114. Biochem Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15674433 Review.
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in signaling plant growth and development.Trends Plant Sci. 2015 Jan;20(1):56-64. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2014.10.001. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Trends Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 25457109 Review.
Cited by
-
The plastidial retrograde signal methyl erythritol cyclopyrophosphate is a regulator of salicylic acid and jasmonic acid crosstalk.J Exp Bot. 2016 Mar;67(5):1557-66. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv550. Epub 2016 Jan 4. J Exp Bot. 2016. PMID: 26733689 Free PMC article.
-
Global gene expression analysis using RNA-seq uncovered a new role for SR1/CAMTA3 transcription factor in salt stress.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 2;6:27021. doi: 10.1038/srep27021. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27251464 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Defense Responses to Biotic Stress and Its Interplay With Fluctuating Dark/Light Conditions.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Mar 4;12:631810. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.631810. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33763093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Responses of OsMPKs in IR56 Rice to Two BPH Populations of Different Virulence Levels.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 13;19(12):4030. doi: 10.3390/ijms19124030. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30551584 Free PMC article.
-
Root Walker: an automated pipeline for large scale quantification of early root growth responses at high spatial and temporal resolution.Plant J. 2024 Jan;117(2):632-646. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16493. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Plant J. 2024. PMID: 37871136 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al. (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Andreasson E, Ellis B. (2010) Convergence and specificity in the Arabidopsis MAPK nexus. Trends Plant Sci 15: 106–113 - PubMed
-
- Asai T, Tena G, Plotnikova J, Willmann MR, Chiu WL, Gomez-Gomez L, Boller T, Ausubel FM, Sheen J. (2002) MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 415: 977–983 - PubMed
-
- Benn G, Wang CQ, Hicks DR, Stein J, Guthrie C, Dehesh K. (August 18, 2014) A key general stress response motif is regulated non-uniformly by CAMTA transcription factors. Plant J http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12620 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bethke G, Pecher P, Eschen-Lippold L, Tsuda K, Katagiri F, Glazebrook J, Scheel D, Lee J. (2012) Activation of the Arabidopsis thaliana mitogen-activated protein kinase MPK11 by the flagellin-derived elicitor peptide, flg22. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 25: 471–480 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

