The multifunctional sorting protein PACS-2 regulates SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of p53 to modulate p21-dependent cell-cycle arrest
- PMID: 25159152
- PMCID: PMC4285392
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.07.049
The multifunctional sorting protein PACS-2 regulates SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of p53 to modulate p21-dependent cell-cycle arrest
Abstract
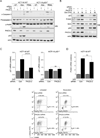
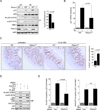
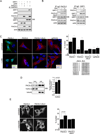
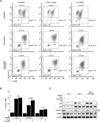
SIRT1 regulates the DNA damage response by deacetylating p53, thereby repressing p53 transcriptional output. Here, we demonstrate that the sorting protein PACS-2 regulates SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of p53 to modulate the DNA damage response. PACS-2 knockdown cells failed to efficiently undergo p53-induced cell-cycle arrest in response to DNA damage. Accordingly, p53 acetylation was reduced both in PACS-2 knockdown cells and thymocytes from Pacs-2(-/-) mice, thereby blunting induction of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 (CDKN1A). The SIRT1 inhibitor EX-527 or SIRT1 knockdown restored p53 acetylation and p21 induction as well as p21-dependent cell-cycle arrest in PACS-2 knockdown cells. Trafficking studies revealed that cytoplasmic PACS-2 shuttled to the nucleus, where it interacted with SIRT1 and repressed SIRT1-mediated p53 deacetylation. Correspondingly, in vitro assays demonstrated that PACS-2 directly inhibited SIRT1-catalyzed p53 deacetylation. Together, these findings identify PACS-2 as an in vivo mediator of the SIRT1-p53-p21 axis that modulates the DNA damage response.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Atkins KM, Thomas L, Youker RT, Harriff MJ, Pissani F, You H, Thomas G. HIV-1 Nef binds PACS-2 to assemble a multikinase cascade that triggers major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) down-regulation: analysis using short interfering RNA and knock-out mice. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:11772–11784. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baptiste-Okoh N, Barsotti AM, Prives C. Caspase 2 is both required for p53-mediated apoptosis and downregulated by p53 in a p21-dependent manner. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:1133–1138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

