Laser Acupuncture at HT7 Acupoint Improves Cognitive Deficit, Neuronal Loss, Oxidative Stress, and Functions of Cholinergic and Dopaminergic Systems in Animal Model of Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 25161693
- PMCID: PMC4138813
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/937601
Laser Acupuncture at HT7 Acupoint Improves Cognitive Deficit, Neuronal Loss, Oxidative Stress, and Functions of Cholinergic and Dopaminergic Systems in Animal Model of Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
To date, the therapeutic strategy against cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease (PD) is still not in satisfaction level and requires novel effective intervention. Based the oxidative stress reduction and cognitive enhancement induced by laser acupuncture at HT7, the beneficial effect of laser acupuncture at HT7 against cognitive impairment in PD has been focused. In this study, we aimed to determine the effect of laser acupuncture at HT7 on memory impairment, oxidative stress status, and the functions of both cholinergic and dopaminergic systems in hippocampus of animal model of PD. Male Wistar rats, weighing 180-220 g, were induced unilateral lesion at right substantianigra by 6-OHDA and were treated with laser acupuncture continuously at a period of 14 days. The results showed that laser acupuncture at HT7 enhanced memory and neuron density in CA3 and dentate gyrus. The decreased AChE, MAO-B, and MDA together with increased GSH-Px in hippocampus of a 6-OHDA lesion rats were also observed. In conclusion, laser acupuncture at HT7 can improve neuron degeneration and memory impairment in animal model of PD partly via the decreased oxidative stress and the improved cholinergic and dopaminergic functions. More researches concerning effect of treatment duration are still required.
Figures
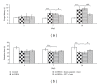




References
-
- Muslimović D, Post B, Speelman JD, Schmand B. Cognitive profile of patients with newly diagnosed Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2005;65(8):1239–1245. - PubMed
-
- Vossius C, Larsen JP, Janvin C, Aarsland D. The economic impact of cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Movement Disorders. 2011;26(8):1541–1544. - PubMed
-
- Svenningsson P, Westman E, Ballard C, Aarsland D. Cognitive impairment in patients with Parkinson's disease: diagnosis, biomarkers, and treatment. The Lancet Neurology. 2012;11(8):697–707. - PubMed
-
- Aarsland D, Brønnick K, Larsen JP, Tysnes OB, Alves G, Norwegian ParkWest Study Group Cognitive impairment in incident, untreated parkinson disease: the Norwegian ParkWest study. Neurology. 2009;72(13):1121–1126. - PubMed
-
- Williams-Gray CH, Evans JR, Goris A, et al. The distinct cognitive syndromes of Parkinson's disease: 5 year follow-up of the CamPaIGN cohort. Brain. 2009;132(11):2958–2969. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

