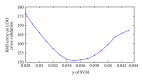
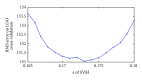
Comparison of two methods forecasting binding rate of plasma protein
- PMID: 25161695
- PMCID: PMC4137739
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/957154
Comparison of two methods forecasting binding rate of plasma protein
Abstract
By introducing the descriptors calculated from the molecular structure, the binding rates of plasma protein (BRPP) with seventy diverse drugs are modeled by a quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) technique. Two algorithms, heuristic algorithm (HA) and support vector machine (SVM), are used to establish linear and nonlinear models to forecast BRPP. Empirical analysis shows that there are good performances for HA and SVM with cross-validation correlation coefficients Rcv(2) of 0.80 and 0.83. Comparing HA with SVM, it was found that SVM has more stability and more robustness to forecast BRPP.
Figures
References
-
- Valladares-Mendez A, Hernández-Núñez E, Cedillo-Rivera R, et al. Synthesis, in vitro and in vivo giardicidal activity, and pharmacokinetic profile of a new nitazoxanide analog. Medicinal Chemistry Research. 2014;23:3157–3164.
-
- Durakovic Z, Vitezic D. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics in the elderly. Periodicum Biologorum. 2013;115:517–520.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical