The search for new amphiphiles: synthesis of a modular, high-throughput library
- PMID: 25161714
- PMCID: PMC4142986
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.10.163
The search for new amphiphiles: synthesis of a modular, high-throughput library
Abstract
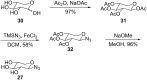
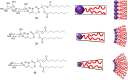
Amphiphilic compounds are used in a variety of applications due to their lyotropic liquid-crystalline phase formation, however only a limited number of compounds, in a potentially limitless field, are currently in use. A library of organic amphiphilic compounds was synthesised consisting of glucose, galactose, lactose, xylose and mannose head groups and double and triple-chain hydrophobic tails. A modular, high-throughput approach was developed, whereby head and tail components were conjugated using the copper-catalysed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) reaction. The tails were synthesised from two core alkyne-tethered intermediates, which were subsequently functionalised with hydrocarbon chains varying in length and degree of unsaturation and branching, while the five sugar head groups were selected with ranging substitution patterns and anomeric linkages. A library of 80 amphiphiles was subsequently produced, using a 24-vial array, with the majority formed in very good to excellent yields. A preliminary assessment of the liquid-crystalline phase behaviour is also presented.
Keywords: amphiphiles; carbohydrates; click chemistry; high throughput; library synthesis.
Figures




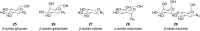



Similar articles
-
The high-throughput synthesis and phase characterisation of amphiphiles: a sweet case study.Chemistry. 2014 Mar 3;20(10):2783-92. doi: 10.1002/chem.201303514. Chemistry. 2014. PMID: 24677204
-
Inverse hexagonal and cubic micellar lyotropic liquid crystalline phase behaviour of novel double chain sugar-based amphiphiles.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017 Mar 1;151:34-38. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.12.004. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017. PMID: 27940167
-
Supramolecular chemistry of pillar[n]arenes functionalised by a copper(i)-catalysed alkyne-azide cycloaddition "click" reaction.Chem Commun (Camb). 2017 May 9;53(38):5250-5266. doi: 10.1039/c7cc01833a. Chem Commun (Camb). 2017. PMID: 28387405
-
CuAAC: An Efficient Click Chemistry Reaction on Solid Phase.ACS Comb Sci. 2016 Jan 11;18(1):1-14. doi: 10.1021/acscombsci.5b00087. Epub 2015 Dec 21. ACS Comb Sci. 2016. PMID: 26652044 Review.
-
Discovery of novel anti-HIV agents via Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) click chemistry-based approach.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016 Sep;11(9):857-71. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2016.1210125. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 27400283 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
