Influence of perylenediimide-pyrene supramolecular interactions on the stability of DNA-based hybrids: Importance of electrostatic complementarity
- PMID: 25161715
- PMCID: PMC4142898
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.10.164
Influence of perylenediimide-pyrene supramolecular interactions on the stability of DNA-based hybrids: Importance of electrostatic complementarity
Abstract
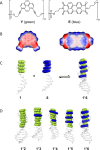
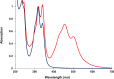
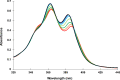
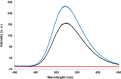
Aromatic π-π stacking interactions are ubiquitous in nature, medicinal chemistry and materials sciences. They play a crucial role in the stacking of nucleobases, thus stabilising the DNA double helix. The following paper describes a series of chimeric DNA-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) hybrids. The PAH building blocks are electron-rich pyrene and electron-poor perylenediimide (PDI), and were incorporated into complementary DNA strands. The hybrids contain different numbers of pyrene-PDI interactions that were found to directly influence duplex stability. As the pyrene-PDI ratio approaches 1:1, the stability of the duplexes increases with an average value of 7.5 °C per pyrene-PDI supramolecular interaction indicating the importance of electrostatic complementarity for aromatic π-π stacking interactions.
Keywords: DNA; hybridization; nucleic acids; perylenediimide; pyrene.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
