Structure/affinity studies in the bicyclo-DNA series: Synthesis and properties of oligonucleotides containing bc(en)-T and iso-tricyclo-T nucleosides
- PMID: 25161745
- PMCID: PMC4142851
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.10.194
Structure/affinity studies in the bicyclo-DNA series: Synthesis and properties of oligonucleotides containing bc(en)-T and iso-tricyclo-T nucleosides
Abstract
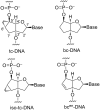
We present the synthesis of the two novel nucleosides iso-tc-T and bc(en)-T, belonging to the bicyclo-/tricyclo-DNA molecular platform. In both modifications the torsion around C6'-C7' within the carbocyclic ring is planarized by either the presence of a C6'-C7' double bond or a cyclopropane ring. Structural analysis of these two nucleosides by X-ray analysis reveals a clear preference of torsion angle γ for the gauche orientation with the furanose ring in a near perfect 2'-endo conformation. Both modifications were incorporated into oligodeoxynucleotides and their thermal melting behavior with DNA and RNA as complements was assessed. We found that the iso-tc-T modification was significantly more destabilizing in duplex formation compared to the bc(en)-T modification. In addition, duplexes with complementary RNA were less stable as compared to duplexes with DNA as complement. A structure/affinity analysis, including the already known bc-T and tc-T modifications, does not lead to a clear correlation of the orientation of torsion angle γ with DNA or RNA affinity. There is, however, some correlation between furanose conformation (N- or S-type) and affinity in the sense that a preference for a 3'-endo like conformation is associated with a preference for RNA as complement. As a general rule it appears that T m data of single modifications with nucleosides of the bicyclo-/tricyclo-DNA platform within deoxyoligonucleotides are not predictive for the stability of fully modified oligonucleotides.
Keywords: DNA/RNA affinity; X-ray structures; nucleic acids; nucleosides; oligonucleotide therapy; oligonucleotides.
Figures

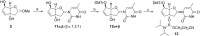


Similar articles
-
6'-Fluoro[4.3.0]bicyclo nucleic acid: synthesis, biophysical properties and molecular dynamics simulations.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2018 Dec 20;14:3088-3097. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.14.288. eCollection 2018. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2018. PMID: 30643586 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and properties of 6'-fluoro-tricyclo-DNA.J Org Chem. 2015 Apr 3;80(7):3556-65. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.5b00184. Epub 2015 Mar 20. J Org Chem. 2015. PMID: 25767996
-
2'β-Fluoro-Tricyclo Nucleic Acids (2'F-tc-ANA): Thermal Duplex Stability, Structural Studies, and RNase H Activation.Chemistry. 2017 Aug 1;23(43):10310-10318. doi: 10.1002/chem.201701476. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Chemistry. 2017. PMID: 28477335
-
Influence of Sugar Modifications on the Nucleoside Conformation and Oligonucleotide Stability: A Critical Review.Chem Rec. 2022 Dec;22(12):e202200174. doi: 10.1002/tcr.202200174. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Chem Rec. 2022. PMID: 36048010 Review.
-
Oligonucleotide n3'-->p5' phosphoramidates and thio-phoshoramidates as potential therapeutic agents.Chem Biodivers. 2010 Mar;7(3):477-93. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.200900187. Chem Biodivers. 2010. PMID: 20232321 Review.
Cited by
-
227 Views of RNA: Is RNA Unique in Its Chemical Isomer Space?Astrobiology. 2015 Jul;15(7):538-58. doi: 10.1089/ast.2014.1213. Astrobiology. 2015. PMID: 26200431 Free PMC article.
-
6'-Fluoro[4.3.0]bicyclo nucleic acid: synthesis, biophysical properties and molecular dynamics simulations.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2018 Dec 20;14:3088-3097. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.14.288. eCollection 2018. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2018. PMID: 30643586 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
