The zinc-binding region (ZBR) fragment of Emi2 can inhibit APC/C by targeting its association with the coactivator Cdc20 and UBE2C-mediated ubiquitylation
- PMID: 25161877
- PMCID: PMC4141206
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fob.2014.06.010
The zinc-binding region (ZBR) fragment of Emi2 can inhibit APC/C by targeting its association with the coactivator Cdc20 and UBE2C-mediated ubiquitylation
Abstract
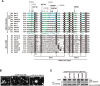
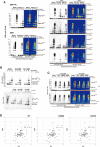
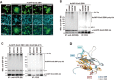
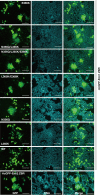
Anaphase-promoting complex or cyclosome (APC/C) is a multisubunit ubiquitin ligase E3 that targets cell-cycle regulators. Cdc20 is required for full activation of APC/C in M phase, and mediates substrate recognition. In vertebrates, Emi2/Erp1/FBXO43 inhibits APC/C-Cdc20, and functions as a cytostatic factor that causes long-term M phase arrest of mature oocytes. In this study, we found that a fragment corresponding to the zinc-binding region (ZBR) domain of Emi2 inhibits cell-cycle progression, and impairs the association of Cdc20 with the APC/C core complex in HEK293T cells. Furthermore, we revealed that the ZBR fragment of Emi2 inhibits in vitro ubiquitin chain elongation catalyzed by the APC/C cullin-RING ligase module, the ANAPC2-ANAPC11 subcomplex, in combination with the ubiquitin chain-initiating E2, E2C/UBE2C/UbcH10. Structural analyses revealed that the Emi2 ZBR domain uses different faces for the two mechanisms. Thus, the double-faced ZBR domain of Emi2 antagonizes the APC/C function by inhibiting both the binding with the coactivator Cdc20 and ubiquitylation mediated by the cullin-RING ligase module and E2C. In addition, the tail region between the ZBR domain and the C-terminal RL residues [the post-ZBR (PZ) region] interacts with the cullin subunit, ANAPC2. In the case of the ZBR fragment of the somatic paralogue of Emi2, Emi1/FBXO5, these inhibitory activities against cell division and ubiquitylation were not observed. Finally, we identified two sets of key residues in the Emi2 ZBR domain that selectively exert each of the dual Emi2-specific modes of APC/C inhibition, by their mutation in the Emi2 ZBR domain and their transplantation into the Emi1 ZBR domain.
Keywords: APC/C; APC/C, anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome; Cdc20; Cdc20, cell-division cycle protein 20; E2C, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 C or UBE2C; Emi2; Emi2, endogenous meiotic inhibitor 2; UBE2C; Ubiquitin ligase activity; ZBR domain; ZBR, zinc-binding region.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Emi2 inhibition of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome absolutely requires Emi2 binding via the C-terminal RL tail.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Mar 15;21(6):905-13. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-11-0974. Epub 2010 Jan 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20089832 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2C: a potential cancer biomarker.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Feb;47:113-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.11.023. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24361302 Review.
-
Emi2-mediated inhibition of E2-substrate ubiquitin transfer by the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome through a D-box-independent mechanism.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Aug 1;21(15):2589-97. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E09-08-0708. Epub 2010 Jun 9. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20534816 Free PMC article.
-
RING E3 mechanism for ubiquitin ligation to a disordered substrate visualized for human anaphase-promoting complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 28;112(17):5272-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504161112. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25825779 Free PMC article.
-
Impressionist portraits of mitotic exit: APC/C, K11-linked ubiquitin chains and Cezanne.Cell Cycle. 2019 Mar-Apr;18(6-7):652-660. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1593646. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Cell Cycle. 2019. PMID: 30874463 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
APC/CCDC20 and APC/C play pivotal roles in the process of embryonic development in Artemia sinica.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 19;6:39047. doi: 10.1038/srep39047. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27991546 Free PMC article.
-
Zn2+ is Essential for Ca2+ Oscillations in Mouse Eggs.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 8:2023.04.13.536745. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.13.536745. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Elife. 2023 Dec 15;12:RP88082. doi: 10.7554/eLife.88082. PMID: 37131581 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Role of zinc in female reproduction.Biol Reprod. 2021 May 7;104(5):976-994. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioab023. Biol Reprod. 2021. PMID: 33598687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zn(2+) at a cellular crossroads.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2016 Apr;31:120-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2016.02.008. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 27010344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zn2+ is essential for Ca2+ oscillations in mouse eggs.Elife. 2023 Dec 15;12:RP88082. doi: 10.7554/eLife.88082. Elife. 2023. PMID: 38099643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998;67:425–479. - PubMed
-
- Deshaies R.J., Joazeiro C.A. RING domain E3 ubiquitin ligases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009;78:399–434. - PubMed
-
- Peters J.M. The anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome: a machine designed to destroy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006;7:644–656. - PubMed
-
- Sullivan M., Morgan D.O. Finishing mitosis, one step at a time. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:894–903. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

