The histone acetyltransferase MOF activates hypothalamic polysialylation to prevent diet-induced obesity in mice
- PMID: 25161885
- PMCID: PMC4142401
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2014.05.006
The histone acetyltransferase MOF activates hypothalamic polysialylation to prevent diet-induced obesity in mice
Abstract
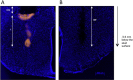
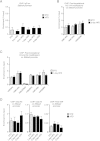
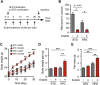
Overfeeding causes rapid synaptic remodeling in hypothalamus feeding circuits. Polysialylation of cell surface molecules is a key step in this neuronal rewiring and allows normalization of food intake. Here we examined the role of hypothalamic polysialylation in the long-term maintenance of body weight, and deciphered the molecular sequence underlying its nutritional regulation. We found that upon high fat diet (HFD), reduced hypothalamic polysialylation exacerbated the diet-induced obese phenotype in mice. Upon HFD, the histone acetyltransferase MOF was rapidly recruited on the St8sia4 polysialyltransferase-encoding gene. Mof silencing in the mediobasal hypothalamus of adult mice prevented activation of the St8sia4 gene transcription, reduced polysialylation, altered the acute homeostatic feeding response to HFD and increased the body weight gain. These findings indicate that impaired hypothalamic polysialylation contribute to the development of obesity, and establish a role for MOF in the brain control of energy balance.
Keywords: Chromatin; Food intake; Hypothalamus; Obesity; Polysialylation; Synaptic plasticity.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Lack of Hypothalamus Polysialylation Inducibility Correlates With Maladaptive Eating Behaviors and Predisposition to Obesity.Front Nutr. 2018 Dec 10;5:125. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2018.00125. eCollection 2018. Front Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30619871 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral cell renewal in adult mice controls the onset of obesity.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 13;8(8):e72029. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072029. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23967273 Free PMC article.
-
Food intake adaptation to dietary fat involves PSA-dependent rewiring of the arcuate melanocortin system in mice.J Neurosci. 2012 Aug 29;32(35):11970-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0624-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22933782 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothalamic neuronal histamine: implications of its homeostatic control of energy metabolism.Nutrition. 1997 May;13(5):403-11. doi: 10.1016/s0899-9007(97)91277-6. Nutrition. 1997. PMID: 9225331 Review.
-
[Hypothalamic inflammation and energy balance deregulations: focus on chemokines.].Biol Aujourdhui. 2016;210(4):211-225. doi: 10.1051/jbio/2016026. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Biol Aujourdhui. 2016. PMID: 28327280 Review. French.
Cited by
-
An assessment of molecular pathways of obesity susceptible to nutrient, toxicant and genetically induced epigenetic perturbation.J Nutr Biochem. 2016 Apr;30:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Oct 23. J Nutr Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27012616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lack of Hypothalamus Polysialylation Inducibility Correlates With Maladaptive Eating Behaviors and Predisposition to Obesity.Front Nutr. 2018 Dec 10;5:125. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2018.00125. eCollection 2018. Front Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30619871 Free PMC article.
-
The Genetic Basis of Childhood Obesity: A Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 15;15(6):1416. doi: 10.3390/nu15061416. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36986146 Free PMC article.
-
The Functional Analysis of Histone Acetyltransferase MOF in Tumorigenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jan 14;17(1):99. doi: 10.3390/ijms17010099. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26784169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain Control of Plasma Cholesterol Involves Polysialic Acid Molecules in the Hypothalamus.Front Neurosci. 2017 May 3;11:245. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00245. eCollection 2017. Front Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28515677 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

