Detection of volume loss in hippocampal layers in Alzheimer's disease using 7 T MRI: a feasibility study
- PMID: 25161900
- PMCID: PMC4141975
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2014.07.011
Detection of volume loss in hippocampal layers in Alzheimer's disease using 7 T MRI: a feasibility study
Abstract
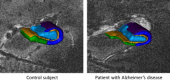
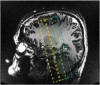
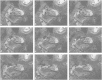
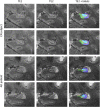
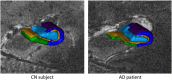
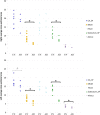
In Alzheimer's disease (AD), the hippocampus is an early site of tau pathology and neurodegeneration. Histological studies have shown that lesions are not uniformly distributed within the hippocampus. Moreover, alterations of different hippocampal layers may reflect distinct pathological processes. 7 T MRI dramatically improves the visualization of hippocampal subregions and layers. In this study, we aimed to assess whether 7 T MRI can detect volumetric changes in hippocampal layers in vivo in patients with AD. We studied four AD patients and seven control subjects. MR images were acquired using a whole-body 7 T scanner with an eight channel transmit-receive coil. Hippocampal subregions were manually segmented from coronal T2*-weighted gradient echo images with 0.3 × 0.3 × 1.2 mm3 resolution using a protocol that distinguishes between layers richer or poorer in neuronal bodies. Five subregions were segmented in the region of the hippocampal body: alveus, strata radiatum, lacunosum and moleculare (SRLM) of the cornu Ammonis (CA), hilum, stratum pyramidale of CA and stratum pyramidale of the subiculum. We found strong bilateral reductions in the SRLM of the cornu Ammonis and in the stratum pyramidale of the subiculum (p < 0.05), with average cross-sectional area reductions ranging from -29% to -49%. These results show that it is possible to detect volume loss in distinct hippocampal layers using segmentation of 7 T MRI. 7 T MRI-based segmentation is a promising tool for AD research.
Keywords: 7 T, 7 Tesla; AD, Alzheimer's disease; Alzheimer's disease; CA, cornu Ammonis; CN, cognitively normal; DG, dentate gyrus; Hippocampal layers; Hippocampus; Human 7 T MRI; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; SP, stratum pyramidale; SRLM, strata radiatum, lacunosum and moleculare; Segmentation; Volumetry.
Figures
References
-
- Albert M.S., DeKosky S.T., Dickson D., Dubois B., Feldman H.H., Fox N.C., Gamst A., Holtzman D.M., Jagust W.J., Petersen R.C., Snyder P.J., Carrillo M.C., Thies B., Phelps C.H. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & Dementia: the Journal of the Alzheimer's Association. 2011;7(3):270–279. 21514249 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chupin M., Lehéricy S., Hasboun D., Colliot O., Goerke U., Marjanska M., Ugurbil K., van der Moortele P.-F. Segmenting the subregions of the human hippocampus at 7 Tesla. NeuroImage. 2009;47:S122.
-
- Chételat G., Fouquet M., Kalpouzos G., Denghien I., De la Sayette V., Viader F., Mézenge F., Landeau B., Baron J.C., Eustache F., Desgranges B. Three-dimensional surface mapping of hippocampal atrophy progression from MCI to AD and over normal aging as assessed using voxel-based morphometry. Neuropsychologia. 2008;46(6):1721–1731. 18289618 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

