Application of principles of exercise training in sub-acute and chronic stroke survivors: a systematic review
- PMID: 25162455
- PMCID: PMC4236657
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-014-0167-2
Application of principles of exercise training in sub-acute and chronic stroke survivors: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: There is increasing evidence for the beneficial effects of exercise training in stroke survivors. In order to reach the desired training effects, exercise training principles must be considered as this ensures the prescription of adequate exercises at an adequate dose. Moreover, exercise training interventions must be designed in a way that maximizes patients' adherence to the prescribed exercise regimen. The objectives of this systematic review were (1) to investigate whether training principles for physical exercise interventions are reported in RCTs for sub-acute and chronic stroke survivors, (2) to evaluate whether the RCTs reported the prescription of the FITT components of the exercise interventions as well as (3) patients' adherence to this prescription, and (4) to assess the risk of bias of the included studies.
Methods: We performed a systematic review of RCTs with exercise training as the primary intervention and muscular strength and/or endurance as primary outcomes. The Cochrane library's risk of bias (ROB) tool was used to judge the methodological quality of RCTs.
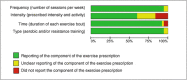
Results: Thirty-seven RCTs were included in this systematic review. Eighteen studies (48.7%) focused on aerobic, 8 (21.6%) on resistance and 11 (29.7%) on combined interventions of aerobic and resistive strength exercise. Twenty-nine studies (78.4%) included only chronic stroke survivors, 5 studies (13.5%) only sub-acute stroke survivors whilst 3 studies (8.1%) included both. In terms of principle of exercise training, 89% reported specificity, 75.7% progression, 48.7% overload, 37.8% initial values, 32.4% reversibility and 13.5% diminishing returns. One RCT described all principles of physical exercise training and 19 (51.4%) all FITT components. Patients' adherence to exercise prescription was accounted for in 3 studies (8.1%). Failure to report blinding in patients and participants and failure to report allocation concealment were the most prevalent methodological shortcomings.
Conclusions: Incomplete and inconsistent reporting of (1) training components, (2) underlying exercise training principles and (3) patient adherence together with (4) a broad variation in the methodological quality of the included RCTs limit both the utility and reproducibility of physical exercise programs in stroke patients.
Figures



References
-
- Koivusalo M, Mackintosh M. The World Health Report 2007. A Safer Future: Global Public Health Security in the 21st Century. World Health Organization, Geneva; 2007.
-
- Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Magid D, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, McGuire DK, Mohler ER, Moy CS, Mussolino ME. et al.Executive summary: heart disease and stroke statistics–2013 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2013;127(1):143–152. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e318282ab8f. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Magid D, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, McGuire DK, Mohler ER, Moy CS, Mussolino ME. et al.Heart disease and stroke statistics–2013 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2013;127(1):e6–e245. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31828124ad. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland; 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

