Tea derived galloylated polyphenols cross-link purified gastrointestinal mucins
- PMID: 25162539
- PMCID: PMC4146515
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105302
Tea derived galloylated polyphenols cross-link purified gastrointestinal mucins
Abstract
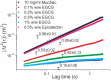
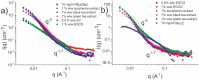
Polyphenols derived from tea are thought to be important for human health. We show using a combination of particle tracking microrheology and small-angle neutron scattering that polyphenols acts as cross-linkers for purified gastrointestinal mucin, derived from the stomach and the duodenum. Both naturally derived purified polyphenols, and green and black tea extracts are shown to act as cross-linkers. The main active cross-linking component is found to be the galloylated forms of catechins. The viscosity, elasticity and relaxation time of the mucin solutions experience an order of magnitude change in value upon addition of the polyphenol cross-linkers. Similarly small-angle neutron scattering experiments demonstrate a sol-gel transition with the addition of polyphenols, with a large increase in the scattering at low angles, which is attributed to the formation of large scale (>10 nm) heterogeneities during gelation. Cross-linking of mucins by polyphenols is thus expected to have an impact on the physicochemical environment of both the stomach and duodenum; polyphenols are expected to modulate the barrier properties of mucus, nutrient absorption through mucus and the viscoelastic microenvironments of intestinal bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Vinson JA, Proch J, Zubik L (1999) Phenol antioxidant quantity and quality in foods: cocoa, dark chocolate, and milk chocolate. J Agric Food Chem 47: 4821–4824 Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10606537. - PubMed
-
- Kishimoto Y, Tani M, Kondo K (2013) Pleiotropic preventive effects of dietary polyphenols in cardiovascular diseases. Eur J Clin Nutr 67: 532–535 Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23403879 Accessed 27 August 2013. - PubMed
-
- El Gharras H (2009) Polyphenols: food sources, properties and applications: A review. Int J Food Sci Technol 44: 2512–2518 Available: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2009.02077.x Accessed 17 December 2012. - DOI
-
- Vuong Q V, Stathopoulos CE, Nguyen MH, Golding JB, Roach PD (2011) Isolation of Green Tea Catechins and Their Utilization in the Food Industry. Food Rev Int 27: 227–247 Available: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/87559129.2011.563397 Accessed 9 May 2013. - DOI
-
- Tsao R (2010) Chemistry and biochemistry of dietary polyphenols. Nutrients 2: 1231–1246 Available: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3257627&tool=p... Accessed 1 November 2012. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

