Zfx facilitates tumorigenesis caused by activation of the Hedgehog pathway
- PMID: 25164012
- PMCID: PMC4199880
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0834
Zfx facilitates tumorigenesis caused by activation of the Hedgehog pathway
Abstract
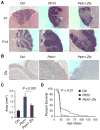
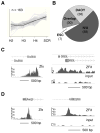
The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway regulates normal development and cell proliferation in metazoan organisms, but its aberrant activation can promote tumorigenesis. Hh-induced tumors arise from various tissues and they may be indolent or aggressive, as is the case with skin basal cell carcinoma (BCC) or cerebellar medulloblastoma, respectively. Little is known about common cell-intrinsic factors that control the development of such diverse Hh-dependent tumors. Transcription factor Zfx is required for the self-renewal of hematopoietic and embryonic stem cells, as well as for the propagation of acute myeloid and T-lymphoblastic leukemias. We report here that Zfx facilitates the development of experimental BCC and medulloblastoma in mice initiated by deletion of the Hh inhibitory receptor Ptch1. Simultaneous deletion of Zfx along with Ptch1 prevented BCC formation and delayed medulloblastoma development. In contrast, Zfx was dispensable for tumorigenesis in a mouse model of glioblastoma. We used genome-wide expression and chromatin-binding analysis in a human medulloblastoma cell line to characterize direct, evolutionarily conserved targets of Zfx, identifying Dis3L and Ube2j1 as two targets required for the growth of the human medulloblastoma cells. Our results establish Zfx as a common cell-intrinsic regulator of diverse Hh-induced tumors, with implications for the definition of new therapeutic targets in these malignancies.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Hooper JE, Scott MP. Communicating with Hedgehogs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:306–17. - PubMed
-
- Ingham PW, Nakano Y, Seger C. Mechanisms and functions of Hedgehog signalling across the metazoa. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12:393–406. - PubMed
-
- Lum L, Beachy PA. The Hedgehog Response Network: Sensors, Switches, and Routers. Science. 2004;304:1755–9. - PubMed
-
- Varjosalo M, Taipale J. Hedgehog: functions and mechanisms. Genes & Development. 2008;22:2454–72. - PubMed
-
- Kenney AM, Cole MD, Rowitch DH. Nmyc upregulation by sonic hedgehog signaling promotes proliferation in developing cerebellar granule neuron precursors. Development. 2003;130:15–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

