Peptidyl arginine deiminase-4 activation exacerbates kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 25164081
- PMCID: PMC4216984
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00243.2014
Peptidyl arginine deiminase-4 activation exacerbates kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury
Abstract
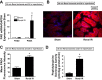
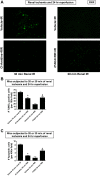
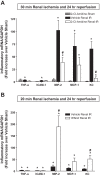
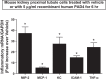
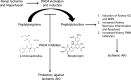
Peptidyl arginine deiminase (PAD)4 is a nuclear enzyme that catalyzes the posttranslational conversion of arginine residues to citrulline. Posttranslational protein citrullination has been implicated in several inflammatory autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, colitis, and multiple sclerosis. Here, we tested the hypothesis that PAD4 contributes to ischemic acute kidney injury (AKI) by exacerbating the inflammatory response after renal ischemia-reperfusion (I/R). Renal I/R injury in mice increased PAD4 activity as well as PAD4 expression in the mouse kidney. After 30 min of renal I/R, vehicle-treated mice developed severe AKI with large increases in plasma creatinine. In contrast, mice pretreated with PAD4 inhibitors (2-chloroamidine or streptonigrin) had significantly reduced renal I/R injury. Further supporting a critical role for PAD4 in generating ischemic AKI, mice pretreated with recombinant human PAD4 (rPAD4) protein and subjected to mild (20 min) renal I/R developed exacerbated ischemic AKI. Consistent with the hypothesis that PAD4 regulates renal tubular inflammation after I/R, mice treated with a PAD4 inhibitor had significantly reduced renal neutrophil chemotactic cytokine (macrophage inflammatory protein-2 and keratinocyte-derived cytokine) expression and had decreased neutrophil infiltration. Furthermore, mice treated with rPAD4 had significantly increased renal tubular macrophage inflammatory protein-2 and keratinocyte-derived cytokine expression as well as increased neutrophil infiltration and necrosis. Finally, cultured mouse kidney proximal tubules treated with rPAD4 had significantly increased proinflammatory chemokine expression compared with vehicle-treated cells. Taken together, our results suggest that PAD4 plays a critical role in renal I/R injury by increasing renal tubular inflammatory responses and neutrophil infiltration after renal I/R.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; apoptosis; citrullination; histone; inflammation; necrosis.
Copyright © 2014 the American Physiological Society.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Peptidyl arginine deiminase-4-deficient mice are protected against kidney and liver injury after renal ischemia and reperfusion.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Aug 1;311(2):F437-49. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00254.2016. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27335376 Free PMC article.
-
Peptidyl arginine deiminase-4 exacerbates ischemic AKI by finding NEMO.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 Jun 1;316(6):F1180-F1190. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00089.2019. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30943066 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil peptidyl arginine deiminase-4 has a pivotal role in ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury.Kidney Int. 2018 Feb;93(2):365-374. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2017.08.014. Epub 2017 Oct 20. Kidney Int. 2018. PMID: 29061334 Free PMC article.
-
PAD4 takes charge during neutrophil activation: Impact of PAD4 mediated NET formation on immune-mediated disease.J Thromb Haemost. 2021 Jul;19(7):1607-1617. doi: 10.1111/jth.15313. Epub 2021 May 12. J Thromb Haemost. 2021. PMID: 33773016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PAD4: pathophysiology, current therapeutics and future perspective in rheumatoid arthritis.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017 Apr;21(4):433-447. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2017.1294160. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017. PMID: 28281906 Review.
Cited by
-
Divergent roles for kidney proximal tubule and granulocyte PAD4 in ischemic AKI.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 May 1;314(5):F809-F819. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00569.2017. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29357426 Free PMC article.
-
Peptidyl arginine deiminase-4-deficient mice are protected against kidney and liver injury after renal ischemia and reperfusion.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Aug 1;311(2):F437-49. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00254.2016. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27335376 Free PMC article.
-
PAD4 Deficiency Leads to Decreased Organ Dysfunction and Improved Survival in a Dual Insult Model of Hemorrhagic Shock and Sepsis.J Immunol. 2018 Mar 1;200(5):1817-1828. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700639. Epub 2018 Jan 26. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29374076 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of peptidylarginine deiminase attenuates inflammation and improves survival in a rat model of hemorrhagic shock.J Surg Res. 2016 Feb;200(2):610-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2015.09.008. Epub 2015 Sep 9. J Surg Res. 2016. PMID: 26434505 Free PMC article.
-
The Fatal Circle of NETs and NET-Associated DAMPs Contributing to Organ Dysfunction.Cells. 2022 Jun 14;11(12):1919. doi: 10.3390/cells11121919. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35741047 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allam R, Scherbaum CR, Darisipudi MN, Mulay SR, Hagele H, Lichtnekert J, Hagemann JH, Rupanagudi KV, Ryu M, Schwarzenberger C, Hohenstein B, Hugo C, Uhl B, Reichel CA, Krombach F, Monestier M, Liapis H, Moreth K, Schaefer L, Anders HJ. Histones from dying renal cells aggravate kidney injury via TLR2 and TLR4. J Am Soc Nephrol 23: 1375–1388, 2012 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anzilotti C, Pratesi F, Tommasi C, Migliorini P. Peptidylarginine deiminase 4 and citrullination in health and disease. Autoimmun Rev 9: 158–160, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Aronson S, Blumenthal R. Perioperative renal dysfunction and cardiovascular anesthesia: concerns and controversies. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 17: 117–130, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Bonventre JV, Weinberg JM. Recent advances in the pathophysiology of ischemic acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 14: 2199–2210, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

