The Chinese herb polyphyllin D sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin-induced growth arrest
- PMID: 25164128
- PMCID: PMC11824142
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-014-1797-x
The Chinese herb polyphyllin D sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin-induced growth arrest
Abstract
Purpose: We evaluated the effects of polyphyllin D (PD), a natural compound with anti-neoplastic activity and a major component of the Chinese herb Paris polyphylla, on ovarian cancer (OVCA) cell line proliferation and platinum sensitivity.
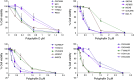
Methods: A panel of 20 OVCA cell lines was subjected to PD treatment, MTS proliferation assays, and determination of IC50. Pre-treatment, baseline genome-wide Affymetrix expression analysis was performed on each cell line, and Pearson's correlation was performed to identify genes associated with OVCA PD sensitivity. Twelve cell lines were treated with PD with and without cisplatin, and the effects of PD on cisplatin IC50 were quantified. Genes associated with OVCA PD sensitivity were evaluated for associations with survival in a publically available clinico-genomic dataset of 218 patients with OVCA.
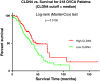
Results: Our results showed that PD exhibited anti-proliferative effects against all OVCA cell lines tested, with IC50 values ranging from 0.2 to 1.4 μm. Furthermore, in all cell lines, PD treatment significantly decreased cisplatin IC50 (mean IC50 reduction of 2.1 µm; P < 0.02). Pearson's correlation test identified 25 probe sets, representing 18 unique genes to be associated with PD sensitivity (FDR = 0). We found that one of these genes was associated with overall survival in women with OVCA: CLDN4 (P = 0.014).
Conclusion: Our findings highlight the value of PD as a natural product with anti-cancer properties, which may also enhance the activity of existing therapeutic agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Agarwal R, D’Souza T, Morin PJ (2005) Claudin-3 and claudin-4 expression in ovarian epithelial cells enhances invasion and is associated with increased matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity. Cancer Res 65:7378–7385. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1036 - PubMed
-
- Baker VV (2003) Salvage therapy for recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 17:977–988 - PubMed
-
- Cheung JY, Ong RC-Y, Suen Y-K et al (2005) Polyphyllin D is a potent apoptosis inducer in drug-resistant HepG2 cells. Cancer Lett 217:203–211. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2004.06.042 - PubMed
-
- Gao M, Cheung KL, Lau IP et al (2012) Polyphyllin D induces apoptosis in human erythrocytes through Ca(2)(+) rise and membrane permeabilization. Arch Toxicol 86:741–752. doi:10.1007/s00204-012-0808-4 - PubMed
-
- Hansen HH, Eisenhauer EA, Hansen M et al (1993) New cytostatic drugs in ovarian cancer. Ann Oncol 4(Suppl 4):63–70 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

