Blood pressure, salivary cortisol, and inflammatory cytokine outcomes in senior female cancer survivors enrolled in a tai chi chih randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 25164513
- PMCID: PMC4344390
- DOI: 10.1007/s11764-014-0395-x
Blood pressure, salivary cortisol, and inflammatory cytokine outcomes in senior female cancer survivors enrolled in a tai chi chih randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Purpose: Older cancer survivors are a vulnerable population due to an increased risk for chronic diseases (e.g., cardiovascular disease) compounded with treatment late-effects and declines in physical functioning. Therefore, interventions that reduce chronic disease risk factors (i.e., blood pressure, chronic inflammation, and cortisol) are important in this population. Tai chi chih (TCC) is a mind-body exercise associated with reductions in chronic disease risk factors, but has not been examined with older cancer survivors. In a feasibility randomized controlled trial of TCC, we examined secondary outcomes of blood pressure, salivary cortisol, and inflammatory cytokines (interleukin (IL)-6, IL-12, tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-10, IL-4) due to their implications in chronic diseases.
Methods: Sixty-three senior female cancer survivors (M age = 67 years, SD = 7.15) with physical functioning limitations (SF-12 physical functioning ≤80 or role-physical ≤72) were randomized to 12-weeks (60-min, three times a week) of TCC or Health Education control (HEC) classes. Resting blood pressure, 1-day salivary cortisol samples, and fasting plasma samples for cytokine multiplex assays were collected at baseline and 1-week post-intervention.
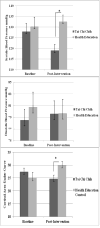
Results: Controlling for baseline values, the TCC group had significantly lower systolic blood pressure (SBP, p = 0.002) and cortisol area-under-curve (AUC, p = 0.02) at post-intervention than the HEC group. There was no intervention effect on inflammatory cytokines (p's > 0.05).
Conclusions: This TCC feasibility trial was associated with significant reductions in SBP and cortisol AUC in senior female cancer survivors. Larger, definitive trials are needed to confirm these findings.
Implications for cancer survivors: Senior survivors' have an increased risk for chronic diseases; however, TCC interventions may help reduce associated risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- ACS. Cancer Treatment and Survivorship Facts & Figures 2012–2013. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2012.
-
- Demark-Wahnefried W, Pinto BM, Gritz ER. Promoting health and physical function among cancer survivors: potential for prevention and questions that remain. JClinOncol. 2006;24(32):5125–31. - PubMed
-
- Rao AV, Demark-Wahnefried W. The older cancer survivor. Crit RevOncolHematol. 2006;60(2):131–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources