Regulatory analysis of the C. elegans genome with spatiotemporal resolution
- PMID: 25164749
- PMCID: PMC4530805
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13497
Regulatory analysis of the C. elegans genome with spatiotemporal resolution
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Regulatory analysis of the C. elegans genome with spatiotemporal resolution.Nature. 2015 Dec 3;528(7580):152. doi: 10.1038/nature16075. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26560031 No abstract available.
Abstract
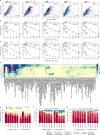
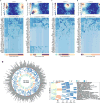
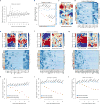
Discovering the structure and dynamics of transcriptional regulatory events in the genome with cellular and temporal resolution is crucial to understanding the regulatory underpinnings of development and disease. We determined the genomic distribution of binding sites for 92 transcription factors and regulatory proteins across multiple stages of Caenorhabditis elegans development by performing 241 ChIP-seq (chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing) experiments. Integration of regulatory binding and cellular-resolution expression data produced a spatiotemporally resolved metazoan transcription factor binding map. Using this map, we explore developmental regulatory circuits that encode combinatorial logic at the levels of co-binding and co-expression of transcription factors, characterizing the genomic coverage and clustering of regulatory binding, the binding preferences of, and biological processes regulated by, transcription factors, the global transcription factor co-associations and genomic subdomains that suggest shared patterns of regulation, and identifying key transcription factors and transcription factor co-associations for fate specification of individual lineages and cell types.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures










Comment in
-
Genomics: Hiding in plain sight.Nature. 2014 Aug 28;512(7515):374-5. doi: 10.1038/512374a. Nature. 2014. PMID: 25164742 No abstract available.
References
-
- Spitz F, Furlong EEM. Transcription factors: from enhancer binding to developmental control. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13:613–626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

