A stepwise approach for effective management of chronic pain in autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease
- PMID: 25165181
- PMCID: PMC4217572
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfu073
A stepwise approach for effective management of chronic pain in autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease
Abstract
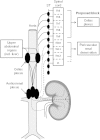
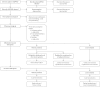
Chronic pain, defined as pain existing for >4-6 weeks, affects >60% of patients with autosomal-dominant polycystic disease (ADPKD). It can have various causes, indirectly or directly related to the increase in kidney and liver volume in these patients. Chronic pain in ADPKD patients is often severe, impacting physical activity and social relationships, and frequently difficult to manage. This review provides an overview of pathophysiological mechanisms that can lead to pain and discusses the sensory innervation of the kidneys and the upper abdominal organs, including the liver. In addition, the results of a systematic literature search of ADPKD-specific treatment options are presented. Based on pathophysiological knowledge and evidence derived from the literature an argumentative stepwise approach for effective management of chronic pain in ADPKD is proposed.
Keywords: ADPKD; management; pain; polycystic kidney disease; polycystic liver disease.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Management of pain in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and anatomy of renal innervation.J Urol. 2015 May;193(5):1470-8. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2014.10.124. Epub 2014 Dec 19. J Urol. 2015. PMID: 25534330 Review.
-
Chronic kidney pain in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a case report of successful treatment by catheter-based renal denervation.Am J Kidney Dis. 2014 Jun;63(6):1019-21. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.12.011. Epub 2014 Feb 8. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014. PMID: 24518126
-
The Association of Combined Total Kidney and Liver Volume with Pain and Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Patients with Later Stage Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease.Am J Nephrol. 2017;46(3):239-248. doi: 10.1159/000479436. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Am J Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28881341 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation and management of pain in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2010 May;17(3):e1-e16. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2010.01.005. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2010. PMID: 20439087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patient-reported outcome measures for pain in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2021 May 27;16(5):e0252479. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252479. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34043715 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and pioglitazone for its therapy: a comprehensive review with an emphasis on the molecular pathogenesis and pharmacological aspects.Mol Med. 2020 Dec 11;26(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s10020-020-00246-3. Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33308138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: an overview of recent genetic and clinical advances.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2492374. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2492374. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40268755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current management of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.World J Nephrol. 2015 Sep 6;4(4):468-79. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v4.i4.468. World J Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 26380198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tolvaptan and Kidney Pain in Patients With Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: Secondary Analysis From a Randomized Controlled Trial.Am J Kidney Dis. 2017 Feb;69(2):210-219. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.08.028. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Am J Kidney Dis. 2017. PMID: 27856088 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pain management in percutaneous nephrolithotomy - an approach rooted in pathophysiology.Nat Rev Urol. 2025 Jun;22(6):354-365. doi: 10.1038/s41585-024-00973-w. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Nat Rev Urol. 2025. PMID: 39806016 Review.
References
-
- Grantham JJ. Clinical practice. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1477–1485. - PubMed
-
- Torres VE, Harris PC, Pirson Y. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet. 2007;369:1287–1301. - PubMed
-
- Oberdhan D, Chapman AB, Davison S, et al. Patient-reported pain in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD): initial concepts based on Patient Focus Group Discussions. 2013 Poster presentation at the American Society of Nephrology Congress, November.
-
- Bajwa ZH, Sial KA, Malik AB, et al. Pain patterns in patients with polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2004;66:1561–1569. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

