Stroke subtype, vascular risk factors, and total MRI brain small-vessel disease burden
- PMID: 25165388
- PMCID: PMC4180484
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000837
Stroke subtype, vascular risk factors, and total MRI brain small-vessel disease burden
Abstract
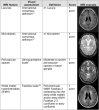
Objectives: In this cross-sectional study, we tested the construct validity of a "total SVD score," which combines individual MRI features of small-vessel disease (SVD) in one measure, by testing associations with vascular risk factors and stroke subtype.
Methods: We analyzed data from patients with lacunar or nondisabling cortical stroke from 2 prospective stroke studies. Brain MRI was rated for the presence of lacunes, white matter hyperintensities, cerebral microbleeds, and perivascular spaces independently. The presence of each SVD feature was summed in an ordinal "SVD score" (range 0-4). We tested associations with vascular risk factors, stroke subtype, and cerebral atrophy using ordinal regression analysis.
Results: In 461 patients, multivariable analysis found that age (odds ratio [OR] 1.10, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.08-1.12), male sex (OR 1.58, 95% CI 1.10-2.29), hypertension (OR 1.50, 95% CI 1.02-2.20), smoking (OR 2.81, 95% CI 1.59-3.63), and lacunar stroke subtype (OR 2.45, 95% CI 1.70-3.54) were significantly and independently associated with the total SVD score. The score was not associated with cerebral atrophy.
Conclusions: The total SVD score may provide a more complete estimate of the full impact of SVD on the brain, in a simple and pragmatic way. It could have potential for patient or risk stratification or early efficacy assessment in clinical trials of interventions to prevent SVD progression and may (after further testing) have a useful role in clinical practice.
© 2014 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Rating total cerebral small-vessel disease: does it add up?Neurology. 2014 Sep 30;83(14):1224-5. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000843. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 25165389 No abstract available.
Summary for patients in
-
The SVD score: a simpler way to assess stroke?Neurology. 2014 Sep 30;83(14):e138-40. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000925. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 25267990 No abstract available.
References
-
- Pantoni L. Cerebral small vessel disease: from pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol 2010;9:689–701 - PubMed
-
- Nitkunan A, Lanfranconi S, Charlton RA, Barrick TR, Markus HS. Brain atrophy and cerebral small vessel disease: a prospective follow-up study. Stroke 2011;42:133–138 - PubMed
-
- Appelman AP, Exalto LG, Van der Graaf Y, Biessels GJ, Mali WP, Geerlings MI. White matter lesions and brain atrophy: more than shared risk factors? A systematic review. Cerebrovasc Dis 2009;28:227–242 - PubMed
-
- Aribisala BS, Valdés Hernández MC, Royle NA, et al. Brain atrophy associations with white matter lesions in the ageing brain: the Lothian Birth Cohort 1936. Eur Radiol 2013;23:1084–1092 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical