Computational genetics analysis of grey matter density in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 25165488
- PMCID: PMC4145360
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0381-7-17
Computational genetics analysis of grey matter density in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
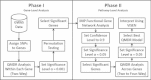
Background: Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of progressive dementia and there is currently no known cure. The cause of onset is not fully understood but genetic factors are expected to play a significant role. We present here a bioinformatics approach to the genetic analysis of grey matter density as an endophenotype for late onset Alzheimer's disease. Our approach combines machine learning analysis of gene-gene interactions with large-scale functional genomics data for assessing biological relationships.
Results: We found a statistically significant synergistic interaction among two SNPs located in the intergenic region of an olfactory gene cluster. This model did not replicate in an independent dataset. However, genes in this region have high-confidence biological relationships and are consistent with previous findings implicating sensory processes in Alzheimer's disease.
Conclusions: Previous genetic studies of Alzheimer's disease have revealed only a small portion of the overall variability due to DNA sequence differences. Some of this missing heritability is likely due to complex gene-gene and gene-environment interactions. We have introduced here a novel bioinformatics analysis pipeline that embraces the complexity of the genetic architecture of Alzheimer's disease while at the same time harnessing the power of functional genomics. These findings represent novel hypotheses about the genetic basis of this complex disease and provide open-access methods that others can use in their own studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular genetics of Alzheimer's disease and aging.Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2005 Jul;27 Suppl A:1-573. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16470248
-
Exploring matrix factorization techniques for significant genes identification of Alzheimer's disease microarray gene expression data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):S7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-S5-S7. Epub 2011 Jul 27. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21989140 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of Alzheimer's disease.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:254954. doi: 10.1155/2013/254954. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23984328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Alzheimer's disease and genetics].Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2013 Aug 6;133(14):1449-52. doi: 10.4045/tidsskr.12.0873. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2013. PMID: 23929292 Review. Norwegian.
-
Genetics of Alzheimer's disease: recent advances.Genome Med. 2009 Mar 27;1(3):34. doi: 10.1186/gm34. Genome Med. 2009. PMID: 19341505 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Revealing third-order interactions through the integration of machine learning and entropy methods in genomic studies.BioData Min. 2024 Jan 30;17(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13040-024-00355-3. BioData Min. 2024. PMID: 38291454 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Imaging Genomics: Integrated Analysis and Machine Learning.Proc IEEE Inst Electr Electron Eng. 2020 Jan;108(1):125-162. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2019.2947272. Epub 2019 Oct 29. Proc IEEE Inst Electr Electron Eng. 2020. PMID: 31902950 Free PMC article.
-
Complex systems analysis of bladder cancer susceptibility reveals a role for decarboxylase activity in two genome-wide association studies.BioData Min. 2016 Dec 12;9:40. doi: 10.1186/s13040-016-0119-z. eCollection 2016. BioData Min. 2016. PMID: 27999618 Free PMC article.
-
The role of visualization and 3-D printing in biological data mining.BioData Min. 2015 Aug 5;8:22. doi: 10.1186/s13040-015-0056-2. eCollection 2015. BioData Min. 2015. PMID: 26246856 Free PMC article.
-
The Application of Artificial Intelligence in the Genetic Study of Alzheimer's Disease.Aging Dis. 2020 Dec 1;11(6):1567-1584. doi: 10.14336/AD.2020.0312. eCollection 2020 Dec. Aging Dis. 2020. PMID: 33269107 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Weiner MW, Veitch DP, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, Cairns NJ, Green RC, Harvey D, Jack CR, Jagust W, Liu E, Morris JC, Petersen RC, Saykin AJ, Schmidt ME, Shaw L, Siuciak JA, Soares H, Toga AW, Trojanowski JQ. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: a review of papers published since its inception. Alzheimers Dement J Alzheimers Assoc. 2012;8(1 Suppl):S1–68. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shen L, Kim S, Risacher SL, Nho K, Swaminathan S, West JD, Foroud T, Pankratz N, Moore JH, Sloan CD, Huentelman MJ, Craig DW, Dechairo BM, Potkin SG, Jack CR Jr, Weiner MW, Saykin AJ. Whole genome association study of brain-wide imaging phenotypes for identifying quantitative trait loci in MCI and AD: A study of the ADNI cohort. NeuroImage. 2010;53:1051–1063. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.01.042. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stein JL, Hua X, Lee S, Ho AJ, Leow AD, Toga AW, Saykin AJ, Shen L, Foroud T, Pankratz N, Huentelman MJ, Craig DW, Gerber JD, Allen AN, Corneveaux JJ, Dechairo BM, Potkin SG, Weiner MW, Thompson P. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Voxelwise genome-wide association study (vGWAS) NeuroImage. 2010;53:1160–1174. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.02.032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

