Corneal epithelial wound healing promoted by verbascoside-based liposomal eyedrops
- PMID: 25165705
- PMCID: PMC4140135
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/471642
Corneal epithelial wound healing promoted by verbascoside-based liposomal eyedrops
Abstract
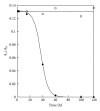
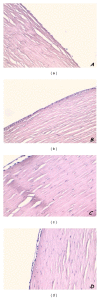
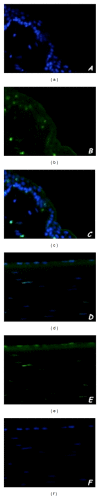
Different liposomal formulations were prepared to identify those capable of forming eyedrops for corneal diseases. Liposomes with neutral or slightly positive surface charge interact very well with the cornea. Then these formulations were loaded with verbascoside to heal a burn of corneal epithelium induced by alkali. The cornea surface affected involved in wound was monitored as a function of time. Experimental results were modeled by balance equation between the rate of healing, due to the flow of phenylpropanoid, and growth of the wound. The results indicate a latency time of only three hours and furthermore the corneal epithelium heals in 48 hours. Thus, the topical administration of verbascoside appears to reduce the action time of cells, as verified by histochemical and immunofluorescence assays.
Figures

References
-
- Costagliola C, Iuliano G, Menzione M, Nesti A, Simonelli F, Rinaldi E. Systemic human diseases as oxidative risk factors in cataractogenesis. I. Diabetes. Ophthalmic Research. 1988;20(5):308–316. - PubMed
-
- Cattaneo F, Iaccio A, Guerra G, Montagnani S, Ammendola R. NADPH-oxidase-dependent reactive oxygen species mediate EGFR transactivation by FPRL1 in WKYMVm-stimulated human lung cancer cells. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2011;51(6):1126–1136. - PubMed
-
- Conti V, Russomanno G, Corbi G, et al. Aerobic training workload affects human endothelial cells redox homeostasis. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 2013;45(4):644–653. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

