Preventive effects of dexmedetomidine on the liver in a rat model of acid-induced acute lung injury
- PMID: 25165710
- PMCID: PMC4138784
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/621827
Preventive effects of dexmedetomidine on the liver in a rat model of acid-induced acute lung injury
Abstract
The aim of this study was to examine whether dexmedetomidine improves acute liver injury in a rat model. Twenty-eight male Wistar albino rats weighing 300-350 g were allocated randomly to four groups. In group 1, normal saline (NS) was injected into the lungs and rats were allowed to breathe spontaneously. In group 2, rats received standard ventilation (SV) in addition to NS. In group 3, hydrochloric acid was injected into the lungs and rats received SV. In group 4, rats received SV and 100 µg/kg intraperitoneal dexmedetomidine before intratracheal HCl instillation. Blood samples and liver tissue specimens were examined by biochemical, histopathological, and immunohistochemical methods. Acute lung injury (ALI) was found to be associated with increased malondialdehyde (MDA), total oxidant activity (TOA), oxidative stress index (OSI), and decreased total antioxidant capacity (TAC). Significantly decreased MDA, TOA, and OSI levels and significantly increased TAC levels were found with dexmedetomidine injection in group 4 (P < 0.05). The highest histologic injury scores were detected in group 3. Enhanced hepatic vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression and reduced CD68 expression were found in dexmedetomidine group compared with the group 3. In conclusion, the presented data provide the first evidence that dexmedetomidine has a protective effect on experimental liver injury induced by ALI.
Figures
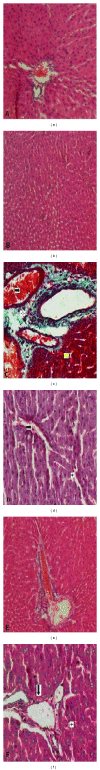
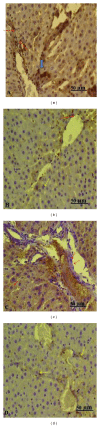
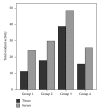
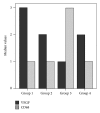
Similar articles
-
Dexmedetomidine and Magnesium Sulfate: A Good Combination Treatment for Acute Lung Injury?J Invest Surg. 2019 Jun;32(4):331-342. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2017.1422575. Epub 2018 Jan 23. J Invest Surg. 2019. PMID: 29359990
-
The protective effects of dexmedetomidine on the liver and remote organs against hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in rats.Int J Surg. 2013;11(1):96-100. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2012.12.003. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Int J Surg. 2013. PMID: 23261946
-
Dexmedetomidine acts as an oxidative damage prophylactic in rats exposed to ionizing radiation.J Clin Anesth. 2016 Nov;34:577-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2016.06.031. Epub 2016 Jul 18. J Clin Anesth. 2016. PMID: 27687454
-
Vitamin C ameliorates high dose Dexmedetomidine induced liver injury.Bratisl Lek Listy. 2016;117(1):36-40. doi: 10.4149/bll_2016_008. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2016. PMID: 26810168
-
Dexmedetomidine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced liver oxidative stress and cell apoptosis in rats by increasing GSK-3β/MKP-1/Nrf2 pathway activity via the α2 adrenergic receptor.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019 Feb 1;364:144-152. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2018.12.017. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30597158
Cited by
-
Dexmedetomidine May Produce Extra Protective Effects on Sepsis-induced Diaphragm Injury.Chin Med J (Engl). 2015 May 20;128(10):1407-11. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.156808. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015. PMID: 25963365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dexmedetomidine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in rats.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Jan;15(1):131-138. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.6012. Epub 2016 Dec 9. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 27959438 Free PMC article.
-
3-Methyladenine and dexmedetomidine reverse lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through the inhibition of inflammation and autophagy.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Apr;15(4):3516-3522. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.5832. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29545877 Free PMC article.
-
Combination therapy of Ulinastatin with Thrombomodulin alleviates endotoxin (LPS) - induced liver and kidney injury via inhibiting apoptosis, oxidative stress and HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB pathway.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):2951-2970. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2024686. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35148668 Free PMC article.
-
Preconditioning rats with three lipid emulsions prior to acute lung injury affects cytokine production and cell apoptosis in the lung and liver.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Feb 5;19(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1137-x. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32024527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- von Dossow-Hanfstingl V. Advances in therapy for acute lung injury. Anesthesiology Clinics. 2012;30(4):629–639. - PubMed
-
- Henrion J, Schapira M, Luwaert R, Colin L, Delannoy A, Heller FR. Hypoxic hepatitis: clinical and hemodynamic study in 142 consecutive cases. Medicine. 2003;82(6):392–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

