Effects of high doses of cholecalciferol in normal subjects: a randomized double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 25166750
- PMCID: PMC4148309
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102965
Effects of high doses of cholecalciferol in normal subjects: a randomized double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Vitamin D repletion with high doses of vitamin D is often recommended to patients and healthy subjects. The safety, especially concerning changes in urinary calcium excretion is of great importance.
Methods: In a double-blinded, placebo-controlled study in 40 healthy volunteers, we examined the changes in mineral metabolism during supplementation with 3000 IU of oral cholecalciferol daily during 4 months.
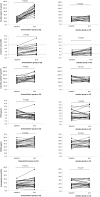
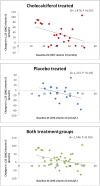
Results: Both 25(OH)vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2vitamin D increased significantly in the active treated group as compared to the placebo group (186% versus 14% (P<0.001) and 28% versus -8% (P<0.001)). No change was observed in urinary calcium excretion in the active group compared to the placebo group (P = 0.891). Fibroblast growth factor 23 increased significantly by 10% (P<0.018) in the active group. However, there was no difference in changes in FGF23 between treatment groups (P = 0.457).
Conclusion: High dose cholecalciferol significantly increases 25(OH)vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2vitamin D levels compared to placebo. No changes in urinary calcium excretion or other measured components of the mineral metabolism were found between groups.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00952562.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Moller UK, Ramlau-Hansen CH, Rejnmark L, Heickendorff L, Henriksen TB, et al. (2006) Postpartum vitamin D insufficiency and secondary hyperparathyroidism in healthy Danish women. Eur J Clin Nutr 60: 1214–1221. - PubMed
-
- Mosekilde L (2005) Vitamin D and the elderly. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 62: 265–281. - PubMed
-
- Mosekilde L, Brot C, Hyldstrup L, Mortensen LS, Moelgaard C, et al. (2005) The vitamin D status of the Danish population needs to be improved. Ugeskr Laeger 167: 895–897. - PubMed
-
- Lips P, Duong T, Oleksik A, Black D, Cummings S, et al. (2001) A global study of vitamin D status and parathyroid function in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: baseline data from the multiple outcomes of raloxifene evaluation clinical trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86: 1212–1221. - PubMed
-
- Lips P, Hosking D, Lippuner K, Norquist JM, Wehren L, et al. (2006) The prevalence of vitamin D inadequacy amongst women with osteoporosis: an international epidemiological investigation. J Intern Med 260: 245–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

