k-t FASTER: Acceleration of functional MRI data acquisition using low rank constraints
- PMID: 25168207
- PMCID: PMC4682483
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.25395
k-t FASTER: Acceleration of functional MRI data acquisition using low rank constraints
Abstract
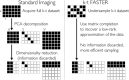
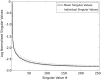
Purpose: In functional MRI (fMRI), faster sampling of data can provide richer temporal information and increase temporal degrees of freedom. However, acceleration is generally performed on a volume-by-volume basis, without consideration of the intrinsic spatio-temporal data structure. We present a novel method for accelerating fMRI data acquisition, k-t FASTER (FMRI Accelerated in Space-time via Truncation of Effective Rank), which exploits the low-rank structure of fMRI data.
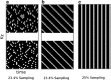
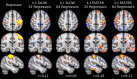
Theory and methods: Using matrix completion, 4.27× retrospectively and prospectively under-sampled data were reconstructed (coil-independently) using an iterative nonlinear algorithm, and compared with several different reconstruction strategies. Matrix reconstruction error was evaluated; a dual regression analysis was performed to determine fidelity of recovered fMRI resting state networks (RSNs).
Results: The retrospective sampling data showed that k-t FASTER produced the lowest error, approximately 3-4%, and the highest quality RSNs. These results were validated in prospectively under-sampled experiments, with k-t FASTER producing better identification of RSNs than fully sampled acquisitions of the same duration.
Conclusion: With k-t FASTER, incoherently under-sampled fMRI data can be robustly recovered using only rank constraints. This technique can be used to improve the speed of fMRI sampling, particularly for multivariate analyses such as temporal independent component analysis.
Keywords: compressed sensing; fMRI; k-t acceleration; low-rank acceleration; matrix completion; resting state networks.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures






References
-
- Frank LR, Buxton RB, Wong EC. Estimation of respiration-induced noise fluctuations from undersampled multislice fMRI data. Magn Reson Med. 2001;45:635–644. - PubMed
-
- Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS. Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1995;34:537–541. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

