A novel deletion mutation in RS1 gene caused X-linked juvenile retinoschisis in a Chinese family
- PMID: 25168411
- PMCID: PMC4274291
- DOI: 10.1038/eye.2014.196
A novel deletion mutation in RS1 gene caused X-linked juvenile retinoschisis in a Chinese family
Erratum in
- Eye (Lond). 2014 Nov;28(11):1394
Abstract
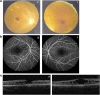
Purpose: X-linked juvenile retinoschisis (XLRS), a leading cause of juvenile macular degeneration, is characterized by a spoke-wheel pattern in the macular region of the retina and splitting of the neurosensory retina. This study aimed to identify the underlying genetic defect in a Chinese family with XLRS.
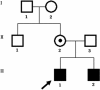
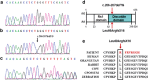
Methods: The proband underwent complete ophthalmic examinations, including fundus examination, fundus autofluorescence, and optical coherence tomography. DNA extracted from proband and his younger brother was screened for mutations in RS1 gene. The detected RS1 mutation was tested in all available family members and 200 healthy controls.
Results: Reduced visual acuity, spoke-wheel pattern at the fovea, and split retina were observed in the proband. A novel frameshift mutation c.206-207delTG in the RS1 gene, leading to a truncated protein (p.L69fs16X), was identified in the proband and his younger brother. This mutation was not found in any unaffected member or in the healthy controls. The mother of the proband was hemizygous for this mutant allele.
Conclusions: We identified a novel causative mutation of RS1 in a Chinese family with XLRS. This finding expands the mutation spectrum of RS1 and provides evidence for a phenotype-genotype study in XLRS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel mutations of the RS1 gene in a cohort of Chinese families with X-linked retinoschisis.Mol Vis. 2014 Jan 31;20:132-9. eCollection 2014. Mol Vis. 2014. PMID: 24505212 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical features of X linked juvenile retinoschisis in Chinese families associated with novel mutations in the RS1 gene.Mol Vis. 2007 Jun 7;13:804-12. Mol Vis. 2007. PMID: 17615541 Free PMC article.
-
Thirty-two years follow-up of X-linked juvenile retinoschisis in a Chinese patient with RS1 mutation.Ophthalmic Genet. 2012 Jun;33(2):77-82. doi: 10.3109/13816810.2011.628359. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Ophthalmic Genet. 2012. PMID: 22171610
-
Of men and mice: Human X-linked retinoschisis and fidelity in mouse modeling.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2022 Mar;87:100999. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.100999. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 34390869 Review.
-
X-linked retinoschisis: mutation spectrum and genotype-phenotype relationship in an Italian pediatric cohort.Ophthalmic Genet. 2023 Feb;44(1):35-42. doi: 10.1080/13816810.2022.2141790. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Ophthalmic Genet. 2023. PMID: 36377647 Review.
Cited by
-
Rs1h-/y exon 3-del rat model of X-linked retinoschisis with early onset and rapid phenotype is rescued by RS1 supplementation.Gene Ther. 2022 Aug;29(7-8):431-440. doi: 10.1038/s41434-021-00290-6. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Gene Ther. 2022. PMID: 34548657 Free PMC article.
-
Requirements for Neurogenin2 during mouse postnatal retinal neurogenesis.Dev Biol. 2018 Oct 15;442(2):220-235. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.07.020. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 30048641 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-exome sequencing identifies an RS1 variant in a Chinese family with X-linked retinoschisis.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Dec;22(6):1406. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10842. Epub 2021 Oct 5. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34675999 Free PMC article.
-
The gene mutation in a Taiwanese family with X-linked retinoschisis.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2015 Jun;31(6):309-14. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2015.03.001. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26043410 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic investigation of 211 Chinese families expands the mutational and phenotypical spectra of hereditary retinopathy genes through targeted sequencing technology.BMC Med Genomics. 2021 Mar 29;14(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12920-021-00935-w. BMC Med Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33781268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sauer CG, Gehrig A, Warneke-Wittstock R, Marquardt A, Ewing CC, Gibson A, et al. Positional cloning of the gene associated with X-linked juvenile retinoschisis. Nat Genet. 1997;17:164–170. - PubMed
-
- Reid SN, Akhmedov NB, Piriev NI, Kozak CA, Danciger M, Farber DB. The mouse X-linked juvenile retinoschisis cDNA: expression in photoreceptors. Gene. 1999;227 (2:257–266. - PubMed
-
- Khan NW, Jamison JA, Kemp JA, Sieving PA. Analysis of photoreceptor function and inner retinal activity in juvenile X-linked retinoschisis. Vision Res. 2001;41 (28:3931–3942. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

